34 Evidence-Based Benefits of Apples
Why Apples
Many of us forget that the simplest answers are often the best.
Reaching for the fruit bowl for some apples is easy since this fruit is very common in both the United States and the rest of the world.
They are also available throughout the year.
It comes as no surprise that apples are good for you, which is why they have earned their reputation for healing in medical circles.
“An apple a day keeps the doctor away” is an old Welsh proverb that most of us have heard.
“What makes this fruit so special?”
Apples are one of the most cultivated and consumed fruits worldwide and praised as a “miracle food.”
Apples are extremely high in important antioxidants, dietary fiber, and flavonoids.
The content of phytonutrients and antioxidants in apples may help reduce the risk of developing cancer, hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease.
These nutrients are found in both the skin and meat of apples, so the whole apple should be eaten for the most benefits.

History
Fall is quickly approaching, and the season delivers not only crisp, autumn air but also our favorite, crisp autumn treat—apples.
Apples have always been part of the human experience.
According to some anthropological research, apples were eaten by early humans.
The Bible in English has Adam and Eve eating an apple, but in Hebrew, it just says that they ate fruit, not what kind.
“Apple” comes from the Old English word æppel and is of Germanic origin.
Roman and Greek mythology refers to the apple as the symbol of love and beauty.
Historians believe that the apple originated in the Dzungarian Alps, a mountain range separating China, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan, where wild apple trees still produce tiny apples.
They think this was possibly about two to ten million years ago when the first humans were evolving.
Others claim, though, that the wild apple arose in the Caucasus Mountains between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea.
Whichever theory is true, as ancient peoples migrated to other lands, they carried apples with them until apples became widespread throughout Asia, the Mediterranean, and the Middle East.
Apples are related to roses, peaches, berries, almonds, and many similar plants.
Early apples may have been smaller and sourer than modern apples — more like crabapples.
Horses, which also lived on the steppes of Central Asia, were eating apples five million years ago.
Still, apples were among the first plants that people planted on purpose.
By 2000 BC, apples were eaten in Greece and Italy, and the Romans brought apples to England about 100 AD.
Apples are not grown in Africa or India, because these areas are too close to the equator.
Apples need cold nights to ripen well.
For ancient and medieval people, apples were the best fruit because they ripened just as the weather was getting cold, and they would keep all winter, meaning you could have food even when nothing was growing.
To make dried apples, people used to slice and dry them in the sun.
They also stored whole apples in underground cold bins.
For making cider, they had a slightly different technique, which involved pressing apples with wooden presses.
When the apple cider ferments with yeast, it becomes a slightly alcoholic drink, and the alcohol preserves the apple juice all winter.
Apple cider was the main alcoholic drink of many peoples in northern Europe.
When the Spaniards and then the English came to North America in the 1600s, they brought apples with them to make apple cider.
All along the East Coast and in the Pacific Northwest, many people treated apple cider as their main drink until Prohibition put the cider orchards out of business.
Apples in the United States
Crabapples came to America before European colonists, but the fruit was far from edible.
The Massachusetts Bay Colony requested cuttings and seeds from England, which were brought over on subsequent voyages to Boston.
Other Europeans brought apple stock to Virginia and the Southwest.
A man from Massachusetts named John Chapman became popular for planting apple trees throughout Ohio, Illinois, and Indiana.
He is better known by his nickname of “Johnny Appleseed.”
As the United States and Canada were settled, nearly every farm grew apples.
Even though some of these apples were very good for eating and cooking, most of the early varieties would be considered poor quality today.
Apples were used for making cider, and those that were ground up were fed to livestock.
Worldwide Sensation
To this day, nearly eight thousand varieties of apples have been identified around the world.
About one hundred varieties are grown in commercial quantity in the United States, with the top ten of those comprising over 90% of the crop.
Modern orchards combine the rich heritage of apple growing with field trials and research to grow an annual United States crop exceeding 220,000,000 bushels.
New varieties are still being cultivated, with the best eventually becoming household names, such as Delicious, McIntosh, Rome, Empire, Cortland, Spartan, and Northern Spy.
Recent arrivals include Honeycrisp, Gala, Fuji, and Liberty, but many older varieties are enjoying a resurgence.
Today’s apples combine the best attributes of the past and present.

How Apples Grow
Also known as Malus Domestica, the apple is a member of the Rosaceae family, and its siblings include plums (Prunus L.), strawberries (Fraaria L.), blackberries (Rubus L.), pears (Pyrus L.), and roses (Rosa L.).
Common characteristics of the family include blossoms with a hypanthium (a floral cup on the flower), five distinct petals, radial symmetry, and many stamen and stipules (leaflike structures).
Recent research has shown that the modern apple we enjoy today started initially with the wild apple species M. sieversii that later intermingled with M. sylvestris (1).
Here are key tips about growing bountiful apple trees for your garden.
How Much Space do You Need For an Apple Tree?
If you have an area one meter square with good light, you have enough space to grow an apple tree, provided you keep it pruned to an upright shape.
Commercially grown apples are pruned as central leader trees.
These varieties are easily contained and capture a lot of light for bud formation and color.
How Often do I Need to Prune?
It is advisable that you prune apples annually, which not only keeps the trees shaped but also balances growth as well as the number of apples.
Should I Prune in the First Year?
Apple trees should be pruned in the first year for the structure of the tree that is strong enough to support the crop.
If you do not prune in the first year, the shoots will bend down or break in the future when too much fruit weighs them down.
Winter Pruning
You should prune in the winter anytime between when leaves start to fall until mid-March.
It is ideal to begin pruning after cold weather so that the stalk has time to harden by January and February, but never prune right after a heavy frost.

Summer Pruning
You should prune from the end of July through the beginning/middle of August.
What is “Establishment Pruning”?
Establishment pruning is an attempt to create a branching framework that is able to hold the potential yields once the tree starts to bear fruit.
Rootstock
Purchasing a tree without knowing the rootstock or with an incorrect rootstock will only cause disappointment.
With no information, you will not know the final size or the degree of growth the trees will eventually achieve.
Favored Forms
The most favored forms are the open center, espalier, cordon, and fan.
The open center form relies on winter pruning, while the others are started by winter pruning and then adapted to summer pruning once the main branch framework is formed.
Where to Buy
It is important to buy apple trees from a good and recognized specialist supplier who will be able to discuss and select the variety/rootstock combination that is ideal for your garden.
Learn to Prune
To know how to prune, you should attend demonstrations that will be of great help in explaining the basics and objectives of pruning.
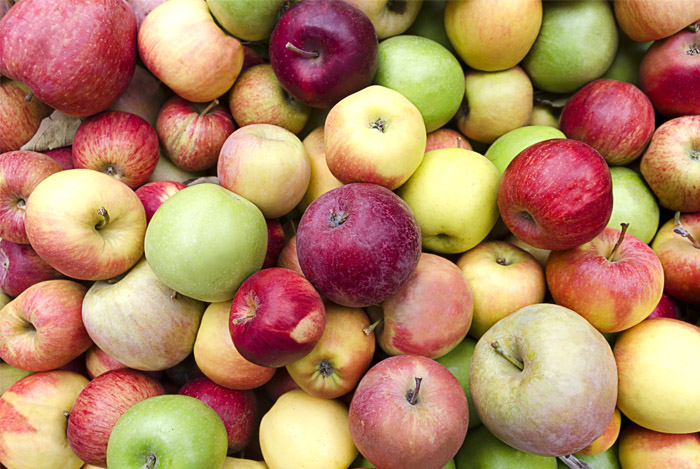

Varieties
Here are nine of the most popular varieties.
Whether you are picking them from the orchard or the produce aisle, you will know what to expect in terms of taste and how best to enjoy them.
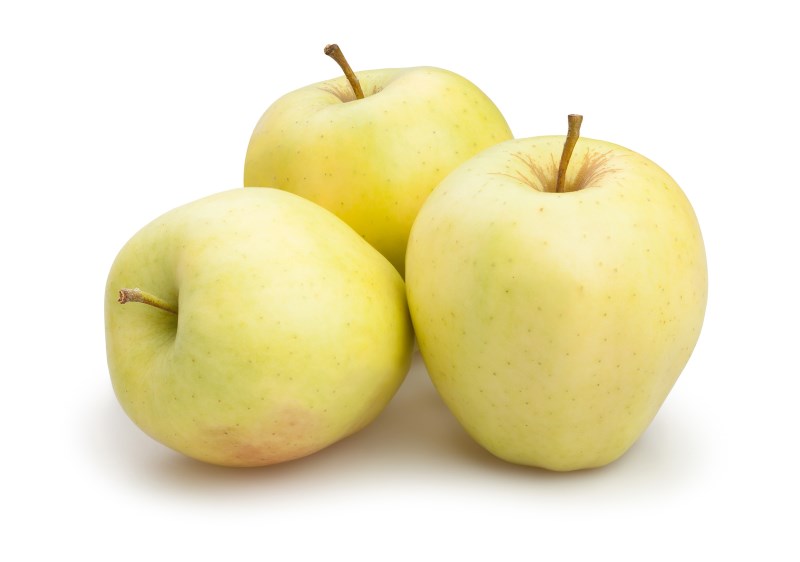

Golden Delicious
Firm in texture and sweet in flavor, Golden Delicious is preferred in cooking circles for its ability to retain shape and rich, juicy flavor when baked or cooked.
The skin is very tender and thin, so it does not require peeling for most recipes.
It is commonly used in fresh salads and freezes well.

Fuji
The spicy, crisp sweetness and firm flesh of Fuji make it an excellent apple.
It is best used in baking or applesauce and stores well.
Fuji skin coloring varies from very red to yellow-green with red highlights.
It was bred from a combination of Ralls Janet and Red Delicious varieties in Japan.

Gala
Known for its freshness, it is shaped like a heart and has distinctive yellow-orange skin with red striping.
Gala is ideal for snacking and salads, good for baking, and very good in applesauce.

Braeburn
This variety has a high-impact flavor.
The crisp, aromatic feel of Braeburn perfectly blends tartness and sweetness, which is just right for salads and snacks.
It is also good in baking, applesauce, and for freezing.
Braeburn color varies from greenish-gold with red spots to nearly solid red.
Braeburn was discovered as a chance seedling near Nelson, New Zealand, in 1952.
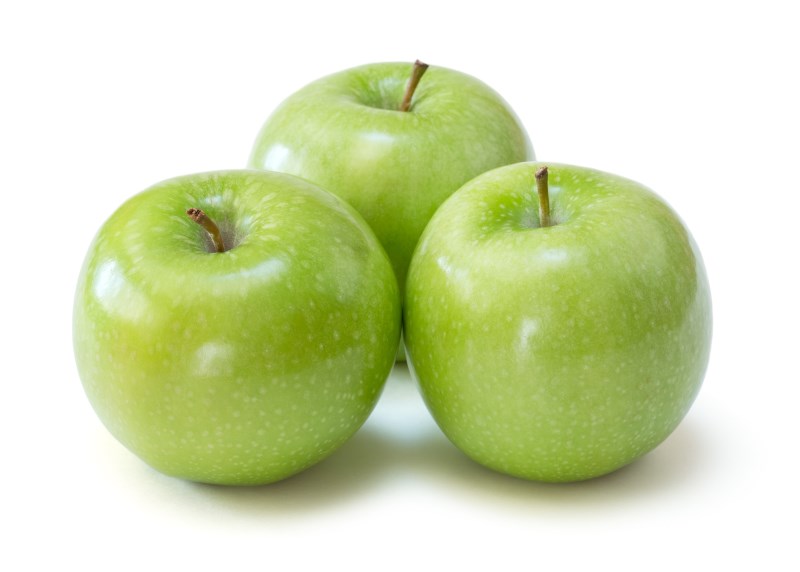

Granny Smith
It is known for its crisp tartness.
It is bright green in color and has a pink blush.
The tartness of Granny Smith really comes through when baked and sautéed.
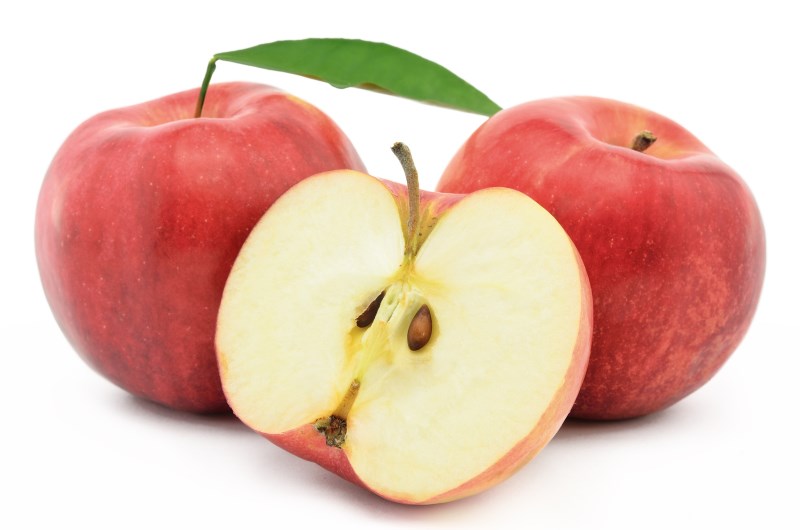

Jonagold
Jonagold is a cross of Jonathan and Golden Delicious apples, offering a unique tangy-sweet taste with firm flesh.
Jonagold is eaten fresh and also used for cooking.
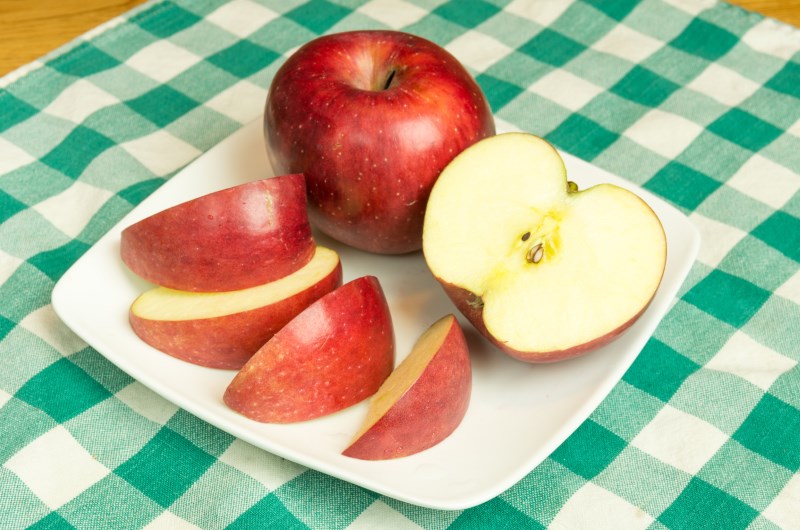

Winesap
This variety is unique for its old-fashioned flavor.
Winesap has a spicy, almost wine-like flavor that makes it the cider maker’s first choice.
It is violet red in color and used as a snack and in salads.
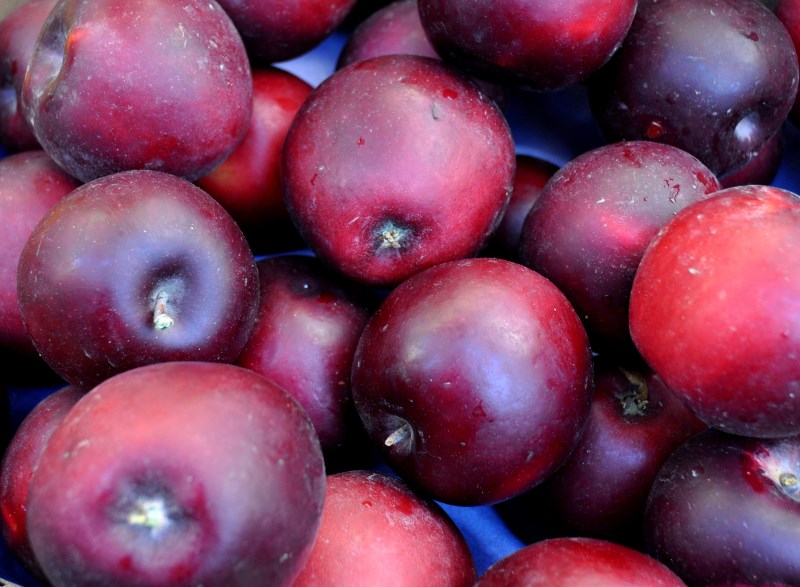

Arkansas Black
It is well named with a deep red, almost black skin.
It is rock hard, tart and sweet, and stores well.

Rome
Rome is the baker’s buddy.
It has a mild flavor that grows richer when baked or sautéed.
Rome has smooth, blazingly red skin with sweet, slightly juicy flesh.

Interesting Facts
Apples not only taste great and are good for your health, but they also have an interesting history.
- The World’s Largest Apple Peel. This record was set by Kathy Wafler Madison on October 16, 1976, in Rochester, New York. It was 172.4 inches long.
- Apple Seeds Contain Poison. Apple seeds contain a cyanide compound. The human body can handle small doses of this naturally occurring poison, so you would have to eat a great number of seeds for it to affect you. Even then, the seeds are covered in a protective coating that keeps the cyanide compound safe inside.
- The Longest-Lived Apple Tree. The longest-lived apple tree in America was reportedly planted in 1647 by Peter Stuyvesant in his Manhattan orchard and was still bearing fruit when a derailed train struck it in 1866.
- Using Apples. In 2005, 36% of apples were used into apple products; 18.6% of them were used for cider and juice, 2% were dried, 2.5% were frozen, 12.2% were canned, and 0.7% were fresh slices. Apples are also used for making baby food, apple butter, vinegar, and jelly.
- National Apple Month. It is the only national generic apple promotion conducted in the United States. Originally founded in 1904 as National Apple Week, it was expanded in 1996 to a three-month promotional period from September through November.
Nutritional Facts
The list of health benefits attributed to apples is long because of the vitamins, minerals, organic compounds, and nutrients present in them.
These important nutritional elements include vitamin C, vitamin K, and riboflavin, as well as such minerals as potassium, manganese, copper, and magnesium.
Apples are also very good sources of dietary fiber, with a single serving providing 12% of the daily fiber requirement.
The real value of apples lies in its organic compounds.
It is rich in phytonutrients and flavonoids, such as quercetin, phloridzin, epicatechin, and various other polyphenic compounds (2).

Health Benefits of Apples
A collection of studies conducted on apples suggests that apples may well be one of the most healthy foods for you to include in your daily diet.
The health benefits of apples include improved digestion, reduced risk of a variety of cancers, heart disease, diabetes, and stroke.
Apples provide prevention of stomach disorders, constipation, gallstones, anemia, liver disorders, diabetes, eye disorders, rheumatism, gout, and much more.
Apples also help improve weakness and provide relief from dysentery.
Moreover, apples can prevent the onset of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease.
Finally, apple aids in skin care and dental care.

Packed With Fiber
Apples are rich in fiber, particularly dietary fiber, containing 12% of the daily fiber requirement.
Fiber is believed to help prevent certain diseases and health problems, such as diabetes, diverticular diseases, and obesity.
The importance of dietary fiber in the human diet has been emphasized in recent years.
However, foods with different fiber composition function differently in the human body.
Therefore, it is important to know the fiber composition of food and how various factors affect fiber content and composition (3).
100 g of apple provides 2,4 g of dietary fiber.

Improve Digestion
The high fiber content in apples helps in the digestive process.
Regular consumption of apples stimulates bowel movement and helps prevent constipation and various stomach disorders.
The fiber found in apples can help you out due to its capacity to either pull water out of your colon to stimulate bowel movement or absorb excess water from your stool to slow your bowels.
It also adds bulk to the stool and stimulates food to pass through the digestive tract smoothly.
It also promotes peristaltic motion, so the muscles contract appropriately and move food along.
According to the World Journal of Gastroenterology, a study conducted in 2012 showed that dietary fiber intake can increase stool frequency in constipated patients (4).
Another digestive problem caused by a lack of fiber is hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoids are a swollen vein in the anal canal, and while not life-threatening, this digestive disorder can be very painful.
They are caused by too much pressure in the rectal and pelvic area.
Fiber can prevent you from straining too much when going to the bathroom, thus helping alleviate hemorrhoids.
In 2006, a study published in the American Journal of Gastroenterology suggested that fiber exhibits a consistent beneficial effect for symptoms and bleeding in the treatment of hemorrhoids (5).
Diarrhea is yet another digestive problem that is inconvenient, unpleasant, and happens to nearly everyone.
When you have diarrhea, your bowel movements are loose and watery.
Many people suffer from diarrhea once or twice each year.
If you have certain conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome, it can occur more often.
Fortunately, you can avoid this common problem in many ways, and one of them is by increasing fiber intake.
Regular consumption of apples may prevent the symptoms of diarrhea.
According to Clinical Nutrition, patients that were fed soluble fiber for six days experienced a reduction in the incidence of diarrhea (6).
Irritable bowel syndrome is characterized by diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain and bloating.
It is recommended that you stay away from dairy and fatty foods while including a high intake of fiber in your diet.
A study reported in 2014 by the American Journal of Gastroenterology in the field of digestive disorders suggested that soluble fiber is effective in treating irritable bowel syndrome (7).

High in Phytochemicals
Diets high in fruits and vegetables may decrease the risk of developing chronic diseases, such as cancer.
Phytochemicals, including flavonoids, phenolics, and carotenoids from fruits and vegetables, may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Apples are a rich source of phytochemicals and have been linked with a reduced risk of some cancers, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and asthma.
Most varieties contain an array of phytochemicals, including catechin, quercetin, phloridzin, and chlorogenic acid, all of which have very strong antioxidant properties.
The fruit has also been found to lower cholesterol, inhibit cancer cell proliferation, and decrease lipid oxidation (8, 9).

Reduce Risk of Cancer
The American Insititute for Cancer Research recommends a high intake of fruits and vegetables, including apples (10).
The role of apples in cancer prevention has been a subject of study for some time.
Results show that the phytochemicals (polyphenols, triterpenoids) and dietary fiber present in apples have been associated with cancer preventive mechanisms in vitro studies (11).
Also, there is a moderate improvement when apples are used to treat various types of cancer, particularly colon and breast cancer, but the most significant discoveries have been regarding lung cancer.
In 2004, French research found that a chemical in apples helps prevent colon cancer (12).
In 2007, a study from Cornell University found compounds called triterpenoids present in apples fight against colon, breast, and liver cancer (13).
The risk of lung cancer can be lowered significantly through the antioxidant composition in apples.
Apples show an undeniable and distinct capacity to reduce lung cancer and slow its spread if it does develop.
A study in Hawaii conducted by the National Cancer Institute found that people who regularly eat apples, white grapefruit, and onions reduce their lung cancer risk in half (14).
According to the journal Planta Medica, apples contain a number of properties that may help in reducing the risk of cancer, including antioxidant activity, antimutagenic activity, antiproliferative and apoptosis-inducing activity, anti-inflammatory mechanisms, as well as mechanisms on epigenetic events and innate immunity (15).

Antioxidants
Since most of the polyphenols in apples function as antioxidants, it is not surprising to see research devoted to studying the health benefits of the antioxidant composition in apples (16).
Particularly strong is the ability of apples to decrease oxidation of cell membrane fats.
This benefit is especially important for your cardiovascular system since oxidation of the fat called lipid peroxidation in the membranes of cells that line your blood vessels is a primary risk factor for clogging of the arteries (atherosclerosis) and other cardiovascular problems (17).
The strong content of antioxidants in apples is also related to its ability to reduce the risk of asthma and lung cancer (18, 19).
In addition to their unusual polyphenol content, apples provide 8 mg of vitamin C.
While the amount is not very high, it is still important mainly because the recycling of vitamin C in the body depends on the presence of flavonoids.

Lower Cholesterol Levels
One medium-sized apple contains about 4 g of fiber.
Insoluble fiber also improves digestion, and apples contain soluble fiber, such as pectin.
This nutrient helps to prevent cholesterol from building up in the lining of blood vessels, which in turn helps in preventing atherosclerosis and heart disease.
Also, pectin blocks absorption of cholesterol, thereby helping the body to use it rather than storing it, according to WebMD (20).
In a 2011 study, Bahram H. Arjmandi, a professor at Florida State University, reported that women who ate 75 g of dried apples on a daily basis for six months had a 23% decrease in LDL-cholesterol.
In addition, the levels of HDL-cholesterol in women increased by about 4% (21).

Lower Risk of Stroke
Stroke is the third leading cause of death in the United States (22), with nearly 130,000 people dying each year.
Fortunately, stroke is wholly preventable, and apples are really important in an anti-stroke diet.
There are several possible reasons for risk reduction.
Fruits such as apples and pears are packed with fiber, which is beneficial for heart health.
They also have a high composition of quercetin, which can reduce inflammation.
Inflammation is linked with hardening of the arteries, which is a risk factor for strokes and heart attacks.
The European Journal of Clinical Nutrition conducted a study in 2000 tracking food consumption among 9,208 people for twenty-eight years.
Patients who ate more apples had a lower risk of stroke.
Researchers suggest that eating apples is associated with a reduced risk of thrombotic stroke due to the presence of the antioxidant flavonoid quercetin (23).
Furthermore, in 2013, Swedish researchers followed 74,961 participants to study the effects of fruit and vegetable consumption on stroke risk.
The results showed that fruit and vegetable consumption, particularly consumption of apples, pears, and green leafy vegetables, was inversely associated with stroke (24).

Promote Heart Health
As mentioned above, apples lower cholesterol levels in your body, thus forming a strong defensive mechanism against cardiovascular disease (25).
The daily dose of an apple required for a healthy heart is approximately one per day, so the saying “an apple a day keeps the doctor away” is more accurate than you would think.
The antioxidant activity in apples reduces the oxidation of fats, called lipid peroxidation, and includes neutralizing triglycerides and various fats found between blood vessels that can exert dangerous pressure.
Moreover, apples contain a very powerful flavonoid called quercetin, present in apple skin, which can reduce inflammation in your blood vessels by reducing the amount of C-reactive protein (26).
This protein has been associated with inflammation of the cardiovascular system, so reducing it through quercetin makes apples very strong heart boosters.
A study from 1993 showed that flavonoids, which are found in vegetables, fruits, and beverages such as tea and wine, may reduce the risk of death from coronary heart disease (27).
Also, high soluble fiber intake has been linked with a slower buildup of cholesterol-rich plaque in your arteries.
The phenolic compound present in apple skin also breaks down cholesterol that gets into the body from solidifying on your artery walls.
Plaque built up inside your arteries decreases blood flow to your heart, causing coronary artery disease (28).

Reduce Risk of Diabetes
The regulation of blood sugar levels is essential for people who suffer from diabetes.
The polyphenol content in apples has been directly linked to reducing the uptake of carbohydrates by the body (29).
This, in turn, reduces the fluctuation of blood sugar levels that occur in the bloodstream, which is an important factor for keeping diabetes in check.
Polyphenols also decrease glucose absorption in the digestive tract, thereby stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas, which is essential to keeping blood sugar levels in check.
The polyphenol composition in apples stimulates the insulin receptors on cells throughout your body, which accelerates the removal of sugar from your bloodstream and gets it to your cells, which are essential for metabolism and proper organ function (30).
Eating whole fruits, but particularly apples, grapes, and blueberries is associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes, according to a new study led by Harvard School of Public Health researchers (31).
Apples are full of polyphenols, which are plant compounds that protect against a variety of chronic diseases, including diabetes.
One of those polyphenols, quercetin, has been found to improve glucose metabolism in liver and skeletal cells (32).
A 2012 study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that apples, as well as blueberries and pears, are associated with a lowered risk of developing type 2 diabetes due to a class of antioxidants, anthocyanins, which are also responsible for red, blue, and purple colors in fruits and vegetables (33).

Avert Respiratory Issues
Eating apples also has respiratory benefits.
Our respiratory system is highly susceptible to inflammation, and an array of respiratory conditions are directly related to inflammation of cells and membranes in that system.
Asthma is probably the most serious condition, as it can be fatal in severe cases.
Apples have shown tremendous anti-inflammatory capacity, and regarding asthma, apples have stood out among other natural treatments, even superseding the benefits of fruit and vegetable consumption in combination.
Namely, five or more apples a week have been linked with better lung function, most likely because of an antioxidant called quercetin present in apple skin (34).
The breath benefits of apples go even further.
A 2007 study published in BMJ found that women who eat apples during are less likely to have children with asthma (35).
In addition, a study of 2,500 middle-aged men in Wales found improved lung function among individuals who ate an apple a day, according to the University of California, Davis (36).

Improve Gut Health
One of the most important and overlooked aspects of human health is the beneficial bacteria residing throughout the entire body.
Apples specifically help in improving the function of bacteria inside your large intestine.
According to a study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry in 2007, apples have been found to change metabolism within the digestive tract and improve the balance of bacteria, leading to maximizing nutrient absorption and eliminating toxins and harmful bacteria (37).

Boost Brain Health
Phytochemicals from apples are important for maintaining the brain’s chemical balance by influencing the function of receptors for the major inhibitory neurotransmitters (38).
Apples have been found to protect neuron cells against oxidative stress and may be a factor in lowering the chance of neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease (39).
A 2006 study published in the journal Experimental Biology and Medicine found that quercetin present in apples is one of two compounds that helped in reducing cellular death caused by inflammation and oxidation of neurons (40).
Apples also contain boron, a compound that has widespread properties in biochemistry and nutrition.
It is important for mineral metabolism and membrane function as well as human brain function and cognitive performance (41).
Apples also increase the amount of acetylcholine in the brain, which is associated with memory, concentration, and problem-solving (42).
According to the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, consumption of foods rich in antioxidants, such as apples, can avert the decline in cognitive performance that accompanies dietary and genetic deficiencies and aging (43).

Apples and Alzheimer’s Disease
There is no doubt that apples have a positive impact on neurological issues, including Alzheimer’s disease.
Thanks to high amounts of phytonutrients in apples, the antioxidant effect of apples is strong and certainly helps in reducing Alzheimer’s disease since brain cell degeneration that causes Alzheimer’s disease has been associated with the free radical activity (44).
According to 2004 research conducted at Cornell University, diets high in antioxidants may be beneficial for protecting brain cells against oxidative stress, a tissue-damaging process associated with Alzheimer’s disease, particularly because these foods are rich in quercetin (45).

Apples and Parkinson’s Disease
The development of Parkinson’s disease is associated with mitochondrial damage in brain cells.
Mitochondria are tiny parts of cells that produce the energy that fuels chemical reactions essential for life.
If mitochondria do not work properly, then energy production is impaired, damaging brain cells and causing them to die prematurely.
Clinical studies have indicated that people with a diet rich in fruits and vegetables are at a lower risk of Parkinson’s disease due to the presence of flavonoids, which are found in apple skin (46).
Flavonoids activate antioxidant enzymes, suppressing the lipid peroxidation, inhibition of inflammatory mediators and oxidative stress, which is the well-accepted concept in the etiology and progression of Parkinson’s disease, according to Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity (47).

High In Vitamin C
A significant portion of vitamin C is contained in apple skin.
Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin important in the development of collagen in your bones, muscles, cartilage, and blood vessels.
Vitamin C supplementation was found to improve the human immune system, such as antimicrobial and natural killer cell activities, according to the Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism (48).
Ascorbic acid also helps in iron absorption as well as fighting colds (49).
It also supports liver function and promotes the production of glutathione, a compound that fights toxins in the liver (50).
Fiber also moves toxins through the intestinal tract and helps prevent them from being circulated to the liver.
Ensuring liver health is a good way to ensure bone health, as a poor liver function has been associated with osteoporosis (51).
One apple provides roughly 10% of your daily recommended allowance for vitamin C.
A raw apple, weighing 138 g with skin, provides 6,3 mg of vitamin C.

Build Stronger Bones
The unique combination of antioxidants, such as flavonoids and polyphenols, plus valuable bone-building minerals is what really makes the apple a bone-healthy powerhouse.
One of the phytonutrients found only in apples is phloridzin, which can help improve bone density and reduce bone breakdown for women after menopause.
Vitamin C has also been found to improve bone mineral density in postmenopausal women (52).
According to Calcified Tissue International, phloridzin consumption may provide protection against osteopenia under inflammation conditions by improving inflammation markers and bone resorption (53).
Boron, a trace mineral found in apples, supports the function of important bone-healthy nutrients, such as calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, and vitamin D (54).
Flavonoids, such as kaempferol, quercetin, and myricetin, have been associated with reducing rheumatoid conditions and inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis and gout, according to the Division of Nutritional Sciences at the University of Nottingham (55).

Boost Immunity
Apples are one of the best immunity-boosting foods due to significant amounts of antioxidants and vitamins, such as vitamin C and beta-carotene.
Vitamin C is very important in the body for building up the body’s natural defense against such substances as disease-causing germs.
German researchers conducted a study in 2009 to prove the function of vitamin C in boosting the immune system and preventing the common cold.
While its capacity to boost immunity is unquestionable, further evidence is needed to determine the therapeutical effects of vitamin C on common cold symptoms (56).
The soluble fiber in apples also boosts immunity due to its anti-inflammatory activity that helps convert pro-inflammatory free radicals into healing anti-inflammatory cells (57).
These altered cells help ward off diabetes and heart disease, which are some of the inflammatory conditions affecting certain body organs.
The soluble fiber in apples, such as pectin, may reduce inflammation and strengthen the immune system (58).

Increase Iron Absorption
With a mere 0,22 mg of iron in a medium-sized apple, apples are not rich in iron.
However, vitamin C present in apples can help absorb iron from other foods eaten at the same meal.
In 2003, the Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine published a study suggesting that children absorb iron well from a meal that includes either orange juice or apple juice (59).
Research presented in the International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research demonstrated that vitamin C in apples and other fruits increases iron absorption in the body by overcoming compounds that hinder absorption (60).

Apples and Liver Toxins
Apples protect your liver from oxidative stress by increasing the production of glutathione, which regulates the cellular balance between oxidation and antioxidation (61).
According to findings that the Physiological Chemistry and Physics and Medical NMR determined, the metabolic cooperation of vitamin C and glutathione decreases oxidative stress, thus improving liver function (62).
Apple consumption also averts gallstone formation.
Gallstones form when there is too much cholesterol in your bile for it to remain a liquid, so it solidifies.
To prevent gallstones, a diet high in fiber and vitamin C is recommended to help you control your weight and cholesterol levels.
Vitamin C increased physical activity and total cholesterol levels, thus reducing the prevalence of gallstones.
This means that vitamin C might exert a protective effect on the development of gallstones (63).

Reduce Risk Of Cataracts
Apples are rich in antioxidant phytonutrients, which can reduce the impact of free radicals on eyesight.
The Department of Human Nutrition and Health in Basel, Switzerland, suggests that people who are on a diet rich in antioxidants reduce the risk of developing cataracts (64).

Stimulate Weight Loss
Aside from the common capacity of fibrous fruits to increase satiety and make us feel full, thus reducing appetite and overeating, apples can help in other ways.
Studies have shown that apples actually boost your metabolism so that additional calories consumed after eating an apple do not register as much in your body, meaning the body burns them off quicker or does not absorb them at all (65).
Apples have also been associated with a reduced risk of obesity in a recent study involving mice at the University of Iowa.
Ursolic acid present in apple skin boosts calorie burn and increases muscle and brown fat (66).

Apples and Dental Care
An apple will not replace your toothbrush, but biting and chewing an apple stimulates the production of saliva in your mouth, thereby reducing tooth decay by lowering levels of bacteria (67).
According to Free Radical Biology & Medicine, apple consumption stimulates the secretion of saliva, which is an alkaline compound that reduces the ability of bacteria to multiply and grow in your mouth (68).

Help with Skin Care
Apples can increase the shine and glow of your skin due to the presence of powerful antioxidants.
These compounds counteract the damaging effects of free radicals that are directly associated with premature aging as well as age spots, wrinkles, and other age-related conditions.
Its boosting effect on circulation also helps keep the skin looking young by keeping blood flow constant to stimulate the replacement of old cells and repair damaged ones.
Dermato Endocrinology in its 2012 review suggests that flavonoids in apples, such as phlorizin, have been demonstrated to have beneficial effects on skin aging (69).

Apples and Magnesium
Magnesium is essential to your health because it is necessary for more than three hundred biochemical reactions in the body.
Roughly 50% of your body’s total magnesium is stored in your bones, while the remaining magnesium is predominantly found in the cells of organs and body tissues.
Magnesium is necessary to keep nerve and muscle function normal and the heart beating rhythmically (70).

Promote Molecule and Enzyme Reactions
Magnesium found in apples has been found to stimulate chemical reactions in the body.
Namely, magnesium is needed to make hundreds of these enzyme reactions function properly.
According to Dr. Carolyn Dean, magnesium is needed for the body to produce and store energy.
Without magnesium, there is no energy, no movement, no life (71).

Apples and Building Muscles
Magnesium contributes to building muscle, both directly and indirectly.
As for its direct function of building muscle, magnesium has been found to exert a positive influence on anabolic hormonal status, including testosterone, in men (72).
Research also indicates that muscle deficiency may not only cause muscle weakness but can also be fatal.
Namely, according to Magnesium Research, a 1991 review of nineteen retrospective case-control studies found that magnesium deficiency reduces exercise capacity and increases the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (73).
In addition, magnesium can increase strength, thus improving the benefits of exercise.
Magnesium has been reported to improve strength development in a 7-week strength training program.
What’s more, it has been shown that magnesium may be important in protein synthesis according to the Journal of the American College of Nutrition (74).

Ease of Chronic and Muscle Pain
Clinical experience has shown that magnesium can be an effective treatment for pain.
A new study on rats published in the Journal of Physiology found that N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA), a brain chemical that triggers nerve pain when overstimulated, can be balanced with magnesium intake without the toxicity (75).
What’s better investigated and has more evidence is the function of magnesium in muscle relief.
Adequate magnesium intake relaxes sore muscles.
By relaxing your muscles, magnesium decreases pain after exercise (76).

Encourage Healthy Pregnancy
Magnesium is important for a baby’s growth and healthy pregnancy.
Adequate magnesium intake increases the pain threshold, optimizes blood circulation, reduces the risk of bone deficiencies, and may prevent eclampsia.
Magnesium also assists in a baby’s nutrition while in utero as well as tissue recovery and growth (77).

Treat Migraines
One of the benefits of magnesium is its capacity to function as a muscle relaxant, thereby being an ideal mineral for individuals suffering from muscle tension, tension headaches, and migraines.
Apples are therefore a good fit for treating migraines due to their magnesium content.
Patients who have chronic migraines are generally deficient in magnesium (78).
According to Cephalalgia: An International Journal of Headache, incorporating high doses of magnesium into your diet appears to be effective in treating migraines (78).

Apples and PMS
Apples are also beneficial for another problem affecting women.
As mentioned above, magnesium relaxes muscles, which contributes to easing cramps and pains caused by premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
One of the symptoms of PMS is mood swings, and many women struggle to find relief at that time of the month.
A 1991 study published in Obstetrics and Gynecology suggests that magnesium supplementation may be effective in treating premenstrual symptoms related to mood changes (79).

Contain Potassium
Potassium, the third most abundant mineral in the human body, is an important compound for improving health.
Aside from being beneficial for blood pressure, stroke, heart, and kidney disorders, potassium also helps maintain water and electrolytic balance (80).

Maintain Water Balance
Potassium helps maintain an optimal fluid balance in the human body.
Different types of cells require a proper water balance for efficient function, and potassium assists these cells in regulating the balance.
Fluid balance is important for the proper functioning of your organs, which is why it is advisable to eat a high-potassium meal after an athletic performance so that you can rehydrate and optimize fluid balance.
The European Journal of Applied Physiology and Occupational Physiology suggested in its 1996 study that post-exercise fluid replacement can be achieved by high potassium intake (81).

Apples and Vitamin K
Vitamin K provides a total balance of eighty nutrients that are vital for the human body.
This mineral is considered to be a fat-soluble vitamin, which is found in your intestines.
According to Open Heart and their recent review from 2015, vitamin K is an anticancer, anti-calcification, bone-forming, and insulin-sensitizing molecule (83).

Help Treat Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder caused by an atypical reaction to gluten, contributing to the degeneration of healthy intestinal tissue.
One of the causes of this health condition is vitamin K deficiency.
In one study, a 4-year-old girl with abdominal distention and signs of malnutrition was given intravenous vitamin K therapy.
The results were normalized, and bruising started to disappear.
The study published in the journal Advances in Therapy shows that vitamin K is efficient in treating patients diagnosed with celiac disease (84).

How to Buy and Store
Look for firm fruits with rich coloring.
Green and yellow apples with a slight blush are best.
Remember that Golden and Red Delicious are among the sweetest apples.
Fuji and Braeburn apples are slightly tart, and Gravenstein, Granny Smith, and Pippin apples are the most tart but retain their texture best when cooked.
In the Northern Hemisphere, apple season starts at the end of summer and lasts until early winter.
Apples available at other times are imported from the Southern Hemisphere or have been in cold storage.
Whole apples are much better than apple juice in terms of nutritional value.
Not only are whole apples higher in dietary fiber, but the common processes of juicing also seem to drastically lower the phytochemical content originally found in the whole fruit.
Apples can be stored for relatively long periods of time, up to three to four months.
Cold storage at low refrigerator temperatures helps minimize the loss of nutrients.
It is also helpful to maintain some moisture in the cold storage area, for instance, by including damp cheesecloth in the crisper bin of a refrigerator.
For several months, polyphenols are completely lost from apples, including both flavonoids and non-flavonoids.
However, valuable amounts of polyphenols are preserved.
Cold storage of apples over the winter months, though, is still considered a key part of dietary nourishment from fruits.
You have probably heard the saying “One bad apple can spoil the whole bunch.”
Well, that is true because bruised apples will start to release unusual amounts of ethylene gas.
This ethylene gas can stimulate the rapid ripening and rotting of other apples, thus decreasing their shelf life.
For that reason, it is recommended that you keep any unusually bruised or soft apples away from other groups of apples stored in bulk.

How to Add More into Your Diet
The skin of apples is unusually high in nutrients, and even if the ingredients of a recipe exclude whole apples, consider omitting apple peeling to reap the unique benefits found in the skin.
Ideally, choose organic apples to avoid problems associated with pesticide residues and other contaminants on the skin.
If you are not in a position to obtain organic apples but are willing to accept some level of risk associated with consumption of residue on the apple skin, we believe it can still be a good trade-off between nutrients and contaminants if you do not peel the apple and leave the skin intact.
Just make sure to thoroughly rinse the entire apple under a stream of pure water while gently scrubbing the skin with a natural bristle brush for ten to fifteen seconds.
To prevent browning when slicing an apple for a recipe, simply put the slices into a bowl of cold water and add a spoonful of lemon juice.
Sliced apples can be preserved well in plastic bags or containers.
Substantial nutrient loss commonly occurs when processing apples into applesauce.
An even great loss of nutrients occurs when processing apples into juice.
Some types of processing are easier on nutrients than others, but applesauce generally requires boiling apples, and apple juices require some extraction of pulp.
In all cases, the more of the apple that can be retained, the better the resulting nourishment.
Processing can be especially harmful to polyphenols.
Only 3% of the catechins and 10% of the flavonoids from whole apples are preserved in processed apple juice.
What’s more, chlorogenic acid, which is one of the most stable polyphenols in apples, is decreased by at least 50% when making apple juice.
These general findings, though, have some exceptions.
For instance, it is possible to put whole apples into a powerful blender and drink the juice.
In this case, very little if any of the nutrients are not preserved.
However, this type of blending is not used in the commercial production of apple juice.
Commercial apple juices are either “cloudy” or “clear.”
Cloudy apple juice typically retains a bit of the pulp composition because although the pulpy composition has been removed from the juice through pressing and filtering, it is added back later.
When purchasing apple juice, always choose cloudy juice if possible.

Precautions
Excessive apple consumption will not cause many side effects, but as with anything eaten in excess, apples may lead to weight gain.
Most apples will have pesticide residue unless they are certified organic.
Although pesticides are found in food at very small trace levels, their negative impact on health is well documented.
The cells’ ability to produce energy, the liver’s ability to process other toxins, and the nerves’ ability to send messages can all be compromised by pesticide exposure.
According to the Environmental Working Group, 98% of conventionally grown apples have pesticide residue on their peels and are among the top 12 fruits and vegetables on which pesticide residue has been found most often (70).
Fortunately, the Colorado State University Extension Service reports that washing apples will help remove pesticides (71).
Taking into consideration all the aforementioned facts, individuals wanting to avoid pesticide-related health risks may want to grow organic apples and avoid eating those that are commercially grown.

Conclusion
An apple is a very healthy, tasty, and popular fruit.
Even though apples are not particularly high in vitamins and minerals, they are a good source of dietary fiber and contain a wide array of organic compounds called phytochemicals.
Regular consumption of apples may improve heart health, reduce the risk of cancer, diabetes, avert respiratory diseases, promote eye health, skin and dental care, and much more.
They may also be helpful for those wanting to lose weight.
If you want to eat healthy, apples are an excellent choice.
FDA Compliance
The information on this website has not been evaluated by the Food & Drug Administration or any other medical body. We do not aim to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any illness or disease. Information is shared for educational purposes only. You must consult your doctor before acting on any content on this website, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, taking medication, or have a medical condition.
HOW WOULD YOU RATE THIS ARTICLE?






I’m so impressed how many health benefits apples have!But how to get my kids to eat at least one apple per day??
You can try some healthy apple snack and desserts recipes. For example, you can grate an apple, add some honey and cinnamon, of course, if your kids don’t have allergy to these products.
So many benefits! I know apples are good for health but I had no idea they can help with so many issues. Thank you for sharing!
Is fiber in apples destroyed when the apple is baked? I give my daughter baked apples rather often, want to be sure she gets all the nutrients.
Ohhh I can’t believe all these benefits! Apples help against cancer? I had no idea, but I’m sure going to eat more apples! I actually got some from the farmers market today, nice and bright red 🙂
Yes! Such a usual fruit, and it has so many not well-known benefits! 🙂
What a wonderful post… informative and well written. I am going to definitely add more apples into my diet and my families as well!
It’s so nice to know that my article encourages people to eat more healthy food! 🙂
Which types of apples are better to eat when trying to lose some weight? I like sweet apples but are they good for me?
Unfortunately, I can’t make my child eat apples. I cooked so many various dishes with apples but he still doesn’t want to eat anything containing apples…How can I make him love apples?
Weight control is one of the best things apple can do. I am quiet impressed with other benefits mentioned within this article. Thanks for sharing..