33 Evidence-Based Strategies to Increase Metabolism Naturally
When people hear the word “metabolism,” many only think of “fast” or “slow”.
While it is true that some people have a faster metabolism that others, it’s not the only important component of this working process.
The speed of your metabolism has a dramatic effect on your ability to lose or gain weight, how much energy you have throughout the day, and it can even determine your risk of encountering diabetes.
What is Metabolism?
Before we get too far into the land of metabolism, it should be noted that the first major step in learning how to change your metabolism begins by actually understanding exactly what it is in the first place.
Dr. Dianna Schwarzbein, writer of The Schwarzbein Principle, stated: “Metabolism is the combined effect of all the varied biochemical processes that continually occur in your body on a cellular level. These processes enable every individual component of your body to function, making it possible for you to think, digest food, move, and perform all the functions of a living, breathing being.”
Are people looking to lose weight the only ones who need to think, digest food, and perform like a living being?
The answer is no – everyone, not solely individuals concerned about their weight, can benefit from a healthy, quick metabolism.
A healthy metabolism ensures that the body is working properly and also allows for less risk of various diseases such as diabetes – a disorder when your metabolism is improperly functioning.
A wellness educator, Denise Baron, explains that a lower metabolism is linked to lower immunity because your body cannot function exactly how, nor as fast as it is supposed to.
Therefore, a lower metabolism actually affects how susceptible you are to common cold and flu viruses.

Interestingly, metabolism is controlled by a tiny, butterfly-shaped gland called the thyroid.
The thyroid is located in the upper neck, near the Adam’s apple and is referred to as a “master control” because the brain can send messages to this gland about bodily processes such as digestion, energy production, and hormone regulation.
Because metabolism plays such a vital role in daily functions, many people are curious as to how to alter their mechanism, hoping for a quick fix in order to shed a few pounds or gain some energy.
Unfortunately, however, changing your metabolism depends on many factors simply because there are many things that determine your individual metabolic rate.
The genetic factors that contribute to determining someone’s metabolism include age, body type, and gender.
Age plays an important role in determining your metabolism – as most people age, they lose muscle and gain fat, which slows down calorie burning.(2)
Additionally, a person’s body size and composition is a big determinant of his or her metabolism because people who are bigger or have more muscle burn more calories than smaller and less muscular people, even if they are simply sitting down.(2)
Finally, men are more likely to have more muscle and less body fat than women of the same age and weight, which, therefore, allows men to burn more calories.
For the most part, individuals do not have a say in how fast or slow their metabolism is because the most prominent factors that determine a person’s metabolism are genetic, like the factors mentioned above.

Fortunately, there are several lifestyle factors such as diet and physical activity, which you are able to control and which can alter your metabolism.
It is critical to point out that simply eating healthy will not have a significant impact on your metabolism.
It is by eating specific foods that an individual will incur a change in the rate of how much energy his or her body can produce.
Certain foods that have been shown to alter metabolism will be discussed later in this piece.
Furthermore, physical activity accounts for a generous portion of the calories that your body burns each day.
However, it is often the most variable factor, as many people will go to the gym one day and then sit all day at work the next.(2)
Since there are many varying components that determine the speed of your metabolism, is it critical to understand that your metabolic rate cannot be held solely responsible for significant weight gain or loss.
That being said, someone with a relatively quick metabolism does not have the luxury of staying slim despite eating junk food and not working out; nor is someone with a slow metabolism doomed to a life of obesity.
The take-home point here is that the speed of your metabolism is largely based on genetic factors and things we cannot change – if we are male or female, old or young, “built” with muscle or more petite.
However, it also depends on how much we work out and what kinds of exercise we perform, how much we eat, and also what we eat.
So many things go into determining metabolism that it cannot be changed by simply altering one of them.
Rather, many things need to be changed if you want to boost your metabolism and, luckily, that is exactly what this article is about.
If it’s dependent on genetics and factors that an individual cannot change, “How is it possible to increase your own metabolism?”, you may ask.
Fortunately, there are many natural activities and methods that have been proven to increase your calorie-burning process.
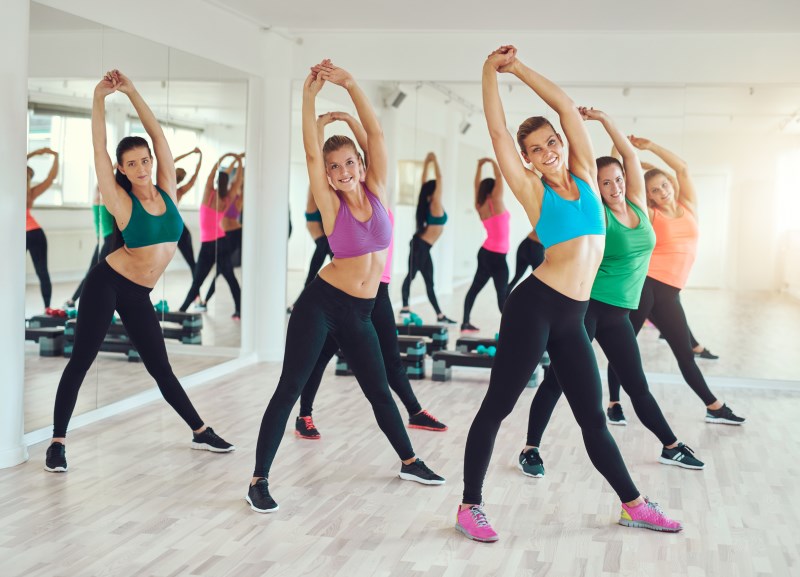
Metabolism and Physical Activity
To begin, it is vital to establish the background behind the importance of exercise/physical activity.
How fast or how slow an individual metabolizes his or her fat is a crucial factor predicting the onset of obesity and diabetes.
Impairments in your metabolism mean you cannot oxidize your body at the appropriate speed and such damage has, interestingly, been shown to predict possible weight gain.
Research has found that “exercise acutely increases fat oxidation, while endurance training increases the capacity to oxidize fat.”(3)
More specifically, endurance training increases the metabolism of fat by boosting mitochondrial density and oxygen delivery to muscles.
Therefore, both activities, either exercising every once in a while or training every day, have shown to boost the ability of the body to metabolize fat, which is critical in maintaining a healthy metabolism.

One relevant study demonstrated how 45 minutes of vigorous physical activity could increase your metabolic rate not only during the activity but afterwards as well.
Knab et al. had ten male subjects complete 2 separate, 24-hour chamber visits, in which one visit consisted of 45-minute exercise, while the other visit was a “rest” day.
After the study was completed, it was discovered that the short, intensive activity on “exercise day” resulted in a net energy expenditure of 519 ± 60.9 kcal (p<0.001).
However, for the 14 hours following the exercise, energy expenditure was increased by 190 ± 71.4 kcal (p<0.001).(4)
With such intriguing results, researchers concluded that for middle-aged males, intense exercise for 45 minutes can elevate the energy expenditures for up to 14 hours after the physical activity is completed.(4)
Such results show that increasing the intensity of your workout for a short period of time continues to reap benefits for your body long after the physical activity is performed.

Additionally, a similar mindset has urged many nutritionist and physical trainers to emphasize the use of high intensity aerobic interval training (HIIT), which is a “compromise between time-consuming moderate-intensity training and sprint-interval training requiring all-out efforts.” (5)
This high intensity aerobic type of exercise has been shown to elevate fat and carbohydrate metabolic capacities in human muscles, especially the skeletal ones.(5)
In a study from the The Journal of Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, the whole body metabolic alterations in “untrained, recreationally active” individuals were observed following six weeks of HIIT for one hour, 3 days a week.
Tests and muscle biopsies were conducted pre-and post-workout.
After the six weeks, researchers discovered that training power output increased by 21% while fat oxidation improved when participants were at 60% of their pre-training peak oxygen consumption.
This meant that participants oxidized more fat during a lower intensity workout compared to when they had first began.(5)
Overall, such a study demonstrated that the 18 hours spent participating in high intensity interval training was a successful method to improve both skeletal muscle as well as whole-body capacities to oxidize fat and carbohydrates in untrained individuals.
Take Home Points:
1. Start working out – the best way to kick-start your metabolism is to simply get off the couch and start moving. Whether that means going to the gym, taking a jog outside, hiking in the mountains, or taking your dog for a walk, any physical activity is better than none.
2. Have intensive workouts every once in a while – studies have shown that increasing the intensity of your workout for a shorter period of time can boost your metabolism more so than a long, monotonous work out. So, instead of strolling around the forest preserve every day, consider forcing yourself to go to the gym once a week and push to give 110% on the Stairmaster or elliptical.
3. Increase the intensity of your workout for a short period of time – an option would be to try interval training. Try to walk, either on a treadmill or outside, for 5 minutes, then sprint for 100 meters. Afterwards, walk for 4 minutes, sprint for 100 more meters, and continue the progression. Getting your heart rate up really quickly during your sprints is extremely beneficial in training your heart and increasing calorie-burning.

Change Your Eating Habits
Don’t Stop Eating
When most people think about diets or weight watching, they think of cutting calories and eating one salad for every meal.
While the overall goal of losing weight is making sure your caloric intake remains less than your energy expenditures, cutting down on calories each day instead of working out more is not the way to do it.
One study sought to question whether cutting calories has a specific effect on metabolic rate or not.
What it discovered was that “dietary-restriction had no effect on mass-specific resting metabolic rate, both when measured as oxygen consumption by respirometry and when measured as heat.” (6)
In other words, eating minimal food each day will not help an individual lose weight, nor increase his or her metabolism.
The explanation behind this is that the body needs the energy from food to drive its metabolic functions.
However, it needs specific types of foods to provide this energy in order to keep functioning as normal – not sweet cakes or greasy fried foods .
When an individual drastically cuts down on calorie intake, the body cannot perform the way it is supposed to and, thereby, does more harm than good to itself.
Smeets and Plantenga conducted a study in which 14 normal-weight women underwent two treatments.
They were given 2 meals (breakfast and dinner) one day, while on a different day, they were given the same amount of food, but divided into three meals (breakfast, lunch, and dinner).(7)
During these days, the women stayed in a respiration chamber in order for researchers to measure energy expenditure and substrate oxidation.
Interestingly, the results depicted that dividing the same amount of energy over three meals instead of two meals increased fat oxidation and increased satiety feelings over 24 hours following the meals.(7)
Researchers concluded that, at least for healthy middle-aged women, “decreasing the inter-meal interval sustains satiety – particularly during the day – and sustains fat oxidation.” (7)
What is demonstrated by this study is the fact that dividing up how and when you eat your food is a factor in how your body processes the energy it stores.
So, not only is eating less food counterproductive, eating more food in one sitting is also detrimental to your body’s metabolic processes.

Cut Down on Trans Fats
Although the recurring theme here has been one of increase (consumption of healthy foods, amount of meals, etc.), there are areas that need to be decreased as well.
One specific example is trans fats. Trans fats are different from the natural fatty acids in plant oils and animal fats.
They are partially hydrogenated vegetable oils with a similar but also very different structure compared to healthy fats.(8)
Furthermore, trans fats are metabolized by the body differently than natural fats.
In a study where piglets consumed hydrogenated trans fats, these fats inhibited the metabolic conversion of linoleic acid (a vital amino acid) to arachidonic acid – a critical conversion.
Previous research had concluded that when linoleic (and arachidonic) acids decrease, mortality rates do as well.(8)
One of the reasons behind this observation has to do with the heart.
The mitochondria in smooth heart muscle cells utilize fatty acids as a source of energy through oxidative phosphorylation in order to continuously pump blood each day.
The trans fatty acids in hydrogenated fats are metabolized much slower than their hydrogenated counterparts.
This makes it much harder for the heart to receive the energy in times of need, such as during a heart attack.(8)
That being said, most nutritionists do not recommend eating any products that contain trans fats which are most usually found in processed food items.

Don’t Skip Breakfast
In addition to what not to consume, there are numerous foods out there that have been shown to help increase a person’s metabolism and it all begins with the most important meal of the day – breakfast.
Dietitians are always stressing the importance of eating breakfast each day because it provides the foundation for your energy levels for the remaining hours of the day.
However, it is pertinent that you consume the right kinds of foods for breakfast instead of simply eating sugary cereals and cakes.
One published study discussed the concept of eating high protein foods and low glycaemic items during breakfast and how it correlates to an individual’s energy level.(9)
It was discovered that eating protein-rich foods in the morning correlated to high levels of energy throughout the day.
Such practice begins controlling your body’s blood-glucose level early on in the day.
Layman suggests that adults need at least 30 grams of protein with each meal “to fully stimulate skeletal muscle protein synthesis.”(9)
Additionally, although they don’t need to be consumed specifically during breakfast, iron-rich foods are also a beneficial choice for those wanting to boost metabolism rates.
Iron is an essential element for humans because it assists metabolic processes such as oxygen and electron transport, and DNA synthesis.
By carrying oxygen to the blood through binding to hemoglobin proteins, iron allows oxygen to be transported throughout the body to enhance metabolic functions that the body must perform.(10)

Start Eating Organic Food
Zinc and calcium are additional elements that are important for bodily functions.
These elements, as well as other minerals and vitamins, have been shown to be extremely abundant in organic foods, making them especially beneficial for your metabolism.
Kesse-Guyot and colleagues examined the benefits that organic foods have on the human body.
By clustering organic consumers versus non-organic consumers of different degrees into groups, the researchers were able to deuce observations about each group.
First of all, they realized that “daily intakes by regular consumers of organic products (RCOP) of both genders were found to receive more minerals and fatty acids, as well as some vitamins and fiber.”
With that being said, Kesse-Guyot and colleagues also discovered that after taking confounding factors into account, both males and females who were regular consumers of organic products had a significantly lower probability of being overweight or obese.
This is in comparison to participants who did not consume organic products.(11)
In addition to natural elements, omega-3’s are similarly favorable for your health because of their polyunsaturated fats. This makes them ideal candidates for natural insulin stabilizers and, therefore, for preventing blood sugar spikes while also increasing satiety.
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fats can easily be found in many fish such as salmon, herring, tuna, and sardines, as well as flaxseed, walnuts, beans, berries, and broccoli.
Finally, one additional food that has been proven to aid in weight loss because of its metabolism-boosting properties is not actually a food at all – rather, it is a spice!
Whether used to season meats or flavor drinks, spicy foods and beverages have recently been found to have thermogenic properties leading to the prevention of a positive energy balance and obesity.
The pungency in spices and certain foods has a stimulatory effect on the sympathetic nervous system which is “involved in the regulation of both sides of the energy balance equation and is an important regulator of energy expenditure.”(13)
In activating the the sympathetic nervous system, spices lead to the increased use of adenosine tri-phosphate (ATP) by the body and, therefore, increase thermogenesis.
To be discussed further, thermogenesis stimulation allows the body to expend more energy in the form of heat, which can compensate for a generous fraction of energy intake each day.
Take Home Points:
1. Don’t cut calorie intake – as already stressed, starving yourself to lose weight will do much more harm than good to your body in the long run. Rather, an appropriate method would be to cut back on eating junk, sugary, or processed food and instead consume larger quantities of protein, fiber, and unsaturated fatty acids.
2. Eat small meals/snacks throughout the day – skipping lunch everyday in order to eliminate calories has convinced most people to over-indulge by eating even more calories during their dinner meal than they would have consumed had they eaten lunch. Lesson learned: don’t skips meals; instead, portion out three appropriately-sized meals each day for yourself.
3. Eat a protein-rich breakfast – protein is the holy-grail of food because of how much energy it requires in order to digest, leading to hundreds of extra calories burned. Protein keeps you feeling fuller for longer. By including protein during breakfast, you are helping to make sure you don’t indulge in unnecessary snacks later in the day.
4. Cut down on trans fats – simply put, don’t eat trans fats. Ideally, a person should not consume any trans fats, but such a recommendation can be difficult because of our reliance on packaged food products.
5. Eat more foods with iron, spice, and omega-3’s – in their own unique way, all three components – iron, spice, and omega -3’s – assist in boosting a person’s metabolism. Making a conscious effort to include foods like salmon, berries, spinach, and beans into your everyday life will certainly benefit you over time.
6. Consider going organic – this doesn’t necessarily mean you have to go completely organic. More so, simply consider purchasing several organic foods rather than their non-organic counterparts. Maybe you will see incredible outcomes and wish to completely immerse yourself in the world of organic foods!

Change Your Drinking Habits
Whether looking for more subtle methods to increase metabolic rate or simply trying to add extra ways to further improve metabolism, focusing on what you put into your body is a critical component of such an endeavor.
Individuals looking to lose weight most commonly turn to strict diets of protein-rich foods and leafy greens.
However, many of these same people forget about the importance of beverages and continue to drink soda, alcohol, and other sugary drinks.
Needless to say, many of those who use this method do not see the results they seek, for obvious reasons.
It must be emphasized that individuals hoping to increase metabolism need not forget about all the benefits, as well as harms, that drinks can bring.
By choosing your beverages wisely, you can greatly improve the calorie-burning process.

Drink More Green Tea
In a study published by The Journal of Zhejiang University Science-B, Chen and Li inspected the benefits of green tea in preventing several diseases.
These included cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and, for the purpose of this piece, Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease.(14)
The US National Cholesterol Education Program states that in order to diagnose metabolic syndrome, an individual must have such things as abdominal obesity, elevated triglyceride level, elevated blood pressure, and several other factors.
Low metabolic rates can be traced back as a likely cause for many of these symptoms and for the overall syndrome, in general.
In an additional study, 63 similar patients with Type 2 diabetes were given a regime of drinking either four cups, two cups, or zero cups of green tea per day for two months.
Researchers found that those patients who drank four cups of green tea per day had significant weight loss (p<0.001), as well as lower systolic blood pressure and body mass index.
Green tea is known to be an excellent source of antioxidants such as catechins and epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG).
These components are hypothesized to “increase thermogenesis [in the body] and 24-hour energy expenditure by about 4%.”(15)
With these energy-consuming processes, it is no wonder that green tea is helpful for increasing your metabolism as well as keeping fat off.

Drink More Coffee
Similar to green tea, coffee has been the topic of recent research concerning its ability to help improve individuals’ metabolism.
Acheson conducted trials in which participants consumed varying dosages of caffeine (such as that found in drinks like coffee, tea, and cocoa) in order to determine its effect on the metabolic rate and substrate utilization in participants of normal weight as well as in obese individuals.
Compared to a placebo, 8 mg/kg of caffeine consumed by normal-weight individuals increased their metabolic rate significantly in the three hours following the caffeine ingestion.(16)
Additionally, fat oxidation also significantly increased during the final hour of testing.
Several other similar tests and procedures were performed with obese individuals, with their metabolic rate increasing during all trials.(16)
Judging by these results, it would seem that consuming coffee/caffeine in reasonable quantities would help individuals in increasing their metabolic rate and/or assist them in weight loss due to increased energy expenditures.

Drink Water
Finally, you must not overlook the powers of the most prevalent beverage there is – water.
Most people already understand the benefits of drinking water to stay hydrated throughout the day, but water also assists with keeping all of your body’s internal processes functioning correctly, which includes your metabolism.
Studies have shown that drinking water can increase resting energy expenditure in both healthy men and women by up to 30% within merely an hour after first drinking the beverage.(17)
Such results are suspected to partially be attributed to water’s thermogenic properties.
With that being said, a study in the International Journal of Obesity set out to prove that similar results could be replicated in obese children.
21 overweight but otherwise healthy children between the ages of 9 and 12 were instructed to drink 10 ml/kg of cold water (4 degrees Celsius).
Resting energy expenditure (REE) was measured before and after water consumption for 66 minutes.
Immediately after drinking the water, REE decreased slightly from the baseline measurement only to significantly increase continually throughout the rest of the 66 minutes.
Maximum energy expenditure was measured around an average of 57 minutes – such a value was 25% higher REE compared to baseline REE.(18)
These findings support the hypothesis that water drinking can assist not only healthy adults, but also overweight children in their attempt to increase metabolism and/or lose weight.
Take Home Points:
1. Drink more green tea – by stimulating the sympathetic nervous system, the ingredients of green tea also induce thermogenesis in the body. Basic chemistry states that in case of most reactions, the higher the temperature, the faster the reaction will proceed. This holds true for your body – at just slightly higher temperature, the body is able to metabolize unwanted calories faster and more efficiently.
2. Drink coffee – when consumed in moderation, coffee also provides the benefit of speeding up metabolic rate. The caffeine in coffee increases metabolic rate, leading to increased fat oxidation. So go ahead and treat yourself to a cup of Joe each morning!
3. Drink plenty of water – cold water is an especially helpful beverage to spark your metabolism. Studies have shown that just by drinking a cup of cold water, you will increase a your resting energy expenditure and actually burn more calories sitting in your chair than you did previously.

Change Your Lifestyle
Get More Sunshine
In addition to being mindful of what you eat and drink on a daily basis, there are also many examples of ways to increase metabolic rate simply by making conscious decisions throughout the day.
One of the easiest decisions to make in terms of helping boost your metabolism is to receive plenty of sun exposure.
Sunlight (and, therefore, vitamin D) is a powerful metabolism stimulator.
The University of Minnesota caught on to the fact that vitamin D intake resulted in an inverse relationship for risk of metabolic syndrome.
As previously discussed, the factors that put a person at risk for such a disease stem from the fact that an individual’s metabolism is running much slower than it should be.
This accumulates into all the symptoms and causes of metabolic syndrome such as high blood pressure, high glucose levels, and abdominal obesity.
In the study, participants were African American and white men and women over the age of 20, with a risk for coronary artery disease.(19)
What researchers found was this: the more vitamin D from dietary and supplemental sources that the subjects received, the lower incidence of metabolic syndrome.
In addition, the study discovered that more vitamin D intake was inversely related to waist circumference and BMI levels.
The reasoning behind these results is thought to be attributed to the fact that “vitamin D is involved in the promotion of the influx of calcium in the regulation of insulin secretion and, therefore, the maintenance of glucose tolerance.”(19)
Regulating insulin allows for your blood-glucose levels to stay balanced throughout the day, preventing sugar spikes and thereby also preventing volatile metabolic activity.
With that said, going outside to soak in the sun every so often sure isn’t such a bad idea, assuming you take proper precautions of protecting yourself.

Try to Avoid Stress
An interesting study published in the Journal of Psychiatric Neuroscience and Therapeutics demonstrated that avoiding stressors and stressful situations can actually lead to an increase in metabolic rate.
The larger the number of stressors exposed to a subject, the more decreased his or her fat oxidation is during the post-meal period when controlled for other outside factors.
Furthermore, this study also discovered an association between prior day stressors and an individual’s postprandial insulin, leading to the hypothesis that today’s stressors can actually predict someone’s insulin levels the next day.(20)
Many previous studies have already discussed and proven the idea that depression and anxiety can lead to weight gain.
Similarly, however, depression and stress can also lead to lower metabolic functioning, which is what likely causes the weight gain seen in so many subjects.
Although these results provide major findings, applying them to everyday life may not be so simple.
Some stressors such as having to pay bills, having a family, and worrying about your kids are inevitable and simply cannot be avoided.
Truthfully, there really is no realistic way for someone to avoid every stressor in his or her life.
There are, nevertheless, ways to both decrease stress and improve metabolism, one of which being an adequate amount of sleep each night.

Get Enough Sleep Time
Sleep has been said to “recharge” our brain and act like a garbage truck, cleaning up all the “waste and garbage” left in our brains throughout the course of the day.
Therefore, getting a proper night’s sleep can help us think more clearly the next day and make wiser decisions, which could possibly lead to lower levels of daily stress.
In fact, one study depicted how a lack of sleep can actually cause alterations in neural activities of our brain.(21)
Participants were subjected to one night of being sleep deprived and one night of complete sleep.
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) techniques were utilized, allowing researchers to view the neural activity in the brains of their subjects both during and after the night of sleep and the night of sleep deprivation.
What researchers found was that compared to sleep, “total sleep deprivation was associated with an increased activation in the right anterior cingulate cortex in response to food images,” which was found to positively correlate with each subject’s appetite ratings.
With these results, researchers concluded that a lack of sleep enhances brain processes underlying the drive to consume food.(21)
Unfortunately, sleep deprivation is oftentimes associated with stress because stressful situations such as a low socioeconomic status or jobs woes inhibit a person’s ability to get a good night’s rest.
Stress is involved in the association between sleep and metabolism through the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.(22)
Not getting enough sleep can lead to HPA axis malfunction, which in turn produces excess glucocorticoids.
Long-term activation of this mechanism has been thought to result in obesity and metabolic syndrome; therefore, it decreased metabolic functioning.(22)
The excess glucocorticoids released during stressful situations increase glucose and insulin levels in the body.
This process, as will be further explained later, is certainly unfavorable for someone attempting to balance his or her metabolism and weight.

Lower Room Temperature
Interestingly, a study conducted by the American Diabetes Association identified a correlation between brown adipose tissue (BAT) and thermogenesis of the human body.(23)
Lee found that “acute cold exposure (hours) increases BAT activity while longer-term exposure (days/weeks) expands BAT volume.”
That being said, the study suggest that BAT could actually impact the whole-body homeostasis, including metabolism.
To this day, exposure to the cold seems to be the best activator of brown adipose tissue and a larger percentage of brown adipose tissue has been proven to correlate with leanness and lower gylcemia in human beings.(23)
So, making sure your thermostat is lowered a couple degrees may in fact help you boost your metabolism in the long run.
Take Home Points:
1. Get some sun exposure (vitamin D) – by helping to regulate insulin secretion like so many other foods and methods, catching some rays (and the vitamin D that goes along with it) can actually help balance your blood sugar. Although it may be difficult to receive significant sun exposure during the winter months, it is important to get your fair share when the sun does come out. There are also vitamin D supplements as well as vitamin D lamps that serve as alternative methods.
2. Avoid stress – understandably, this is much easier said than done. There are many unavoidable stressors throughout everyone’s day that just can’t be avoided. Therefore, it is imperative to stay clear of the stress that you can avoid such as fights with your spouse because of your own irritability or worrying about a research paper due because you didn’t plan ahead. By thinking ahead and keeping a level mind, some stress can be avoided.
3. Get enough sleep – to help avoid the stress mentioned above, it is vital that you get an adequate amount of sleep each night. The phrase “sleep on it” is widely used for a reason – getting a good night’s rest quite literally clears your mind and promotes healthy behaviors.
4. Turn down the temperature – a good idea would be to turn down your thermostat before you go to bed because you will likely not feel the temperature difference when you are sleeping. Exposing yourself to cooler temperatures seems counterproductive after the thermogenesis of the body has been reiterated. Nevertheless, short bursts of a cold environment activate your brown adipose tissue, which then actually generates body heat. Therefore, you are helping to heat up your body and increase fat burning either way.
Foods That Help Boost Metabolism

Almonds
Almonds, like most nuts, contain a lot of fiber, a lot of fatty acids, and a lot of calories.
However, almonds actually contain more of these special fatty acids compared to other nuts.
This kind of fat is natural, meaning that your body can easily burn it off for fuel instead of storing it.
Because of this, almonds spark your body into a “fat-burning” mode and your metabolism begins to look for other sources of fat to burn because it burns this fat away so easily.
Since almonds are calorie-rich, most dietitians warn against eating too many in order to avoid making the process of burning calories counterproductive.

Beans
Since it takes more calories to digest dietary proteins than any other nutrient, when someone consumes more protein, he or she will naturally begin to burn more calories throughout the day.
Kristen Trukova, a clinical oncology dietitian, states that “consuming 400 calories of protein will require about 80 calories to digest it, compared with only around 40 calories for carbohydrates and 12 calories required for fat digestion of the same amount of food.”
There is no denying that beans are packed with protein, but their abundance of additional fiber makes beans an ever better choice for increasing your metabolism.
Furthermore, beans are rich in iron – a mineral that transports oxygen to muscles throughout the body, which is required in order to burn fat.
In other words, iron assists the body in making energy, so eating beans is essentially helping your body make more energy.

Berries
Fruits, in general, are significant sources of healthy carbohydrates and fiber which are two nutrients that are extremely important for increasing metabolism.
The human body cannot technically digest fiber, but in an effort to try and digest it anyways, we burn calories in the process.
1 cup of raspberries actually contains an amazing 8 g of fiber while only containing 60 calories.
This fiber acts as an absorber by soaking up the fats and calories from the other foods we eat, and removes them from the digestive system before our bodies can entirely process them.
However, berries, specifically, contain antioxidants in addition to their carbs and fiber.
Antioxidants such as vitamin C help offset the effect on free radicals in the body when we exercise.
They, therefore, have somewhat of a “healing” power, helping our bodies regain their full, calorie-burning potential so we can get back on our feet and work out sooner rather than later.

Bone Broth
Bone broth is, most simply, the liquefied bones of meat.
As intimidating as such a definition may seem, it is important to note that bone broth is actually an extremely efficient metabolism booster due to its protein, minerals, and collagen.
The collagen helps the body by enhancing the mucus barrier in the stomach, allowing for healthy and strong digestion as well as enhancing the integration of nutrients.
The lining of the intestines is normally permeable to allow for the flow of nutrients into the bloodstream.
However, due to such factors like poor diet, stress, and infections, “holes” can form in this barrier and allow undigested food to flow through it.
This process can quickly lead to autoimmune problems and also limits the amount of properly digested nutrients your body is receiving.
The gelatin in bone broth essentially patches and repairs these holes in the intestinal lining so the proper absorption of nutrients can proceed.

Celery
Many people consider celery a “negative-calorie” food because it requires more energy to eat and digest than what you get from the food itself.
Whether this statement holds true, there is no denying that celery has a very small amount of calories.
When you chew celery, you activate your digestive system, but you are also adding water to your body because celery is a vegetable containing large amounts of water.
As previously mentioned, water is an essential key for keeping the body stable and healthy.
Since over 70% of our body consists of water, when we don’t get enough of it, our bodies are forced to store excess fats and slow down their metabolism in order to conserve energy.
Therefore, the hydration that accompanies the consumption of celery is an essential component of bettering your metabolism.

Chia Seeds
Packed with fiber, protein, and omega-3’s, chia seeds are the holy grail of metabolism boosting.
The fiber improves digestion by balancing hormone levels such as insulin to even out your blood sugar.
The protein, as stated previously, takes lots of energy to digest and, therefore, burns calories when you consume it.
Additionally, chia seeds are said to contain more omega-3’s than salmon – an incredible feat for such a tiny seed because omega-3 fatty acids aid in the efficiency of your metabolism.(25)
The importance of omega-3’s stems from the fact that these fatty acids help increase the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamin A, D, E, and K.

Chocolate
Most specifically, dark chocolate has been proven to help boost your metabolism mainly because of its complete source of magnesium.
Magnesium from raw cacao supports healthy glucose levels, which is vital in maintaining balanced blood sugar and avoiding sudden blood sugar spikes.
Furthermore, magnesium also stimulates a hormone called adiponectin, which helps burn the fat stored in the body.
Therefore, consumption of dark chocolate with 70% or higher cacao allows your metabolism to burn up extra fat and maintain a healthy amount of glucose throughout your body.

Apple Cider Vinegar
Unlike most other foods and drinks recommended to boost metabolism, apple cider vinegar benefits your body by enhancing your stomach’s ability to produce hydrochloric acid.
Hydrochloric acid is a chemical that breaks down all the food in your stomach, which means that the more hydrochloric acid produced, the easier and faster your stomach is able to digest and break down food.
Such a process leads to better absorption of the nutrients essential for keeping the body healthy.
Additionally, just like chocolate, apple cider vinegar also helps to balance out your blood sugar level.
Doing so aids in eliminating food cravings throughout the day because your blood maintains a stable amount of sugar during the entire day.

Cinnamon
Cinnamon is widely accepted by almost all scientists and nutritionists as a metabolism booster.
The key component of this common spice are its thermogenic properties.
This means that once you consume it, your body begins to burn calories and continues to do so throughout the entire day; even as little as ¼ teaspoon can kick-start the process.
Cinnamon, in particular, targets carbohydrates and forces your metabolism to effectively burn this type of energy.
However, it also plays a role in balancing your cravings throughout the day.
Cinnamon imitates the activity of insulin by regulating blood-sugar levels and thereby preventing excess fat to be stored away.
In doing so, cinnamon makes sure that your body is not storing any more fat than it actually needs to.

Citrus Fruits
At any sign of catching a cold, most people run to the store to retrieve vitamin C supplements, a bottle of orange juice, or a couple of citrus fruits.
We all know that citrus fruits like kiwis, oranges, limes, and grapefruit carry an incredible amount of this vitamin.
This is important for boosting our immune systems to fight away any viruses or bacteria that may have entered our bodies.
However, citrus fruits actually benefit our bodies in another way too – by helping us metabolize fat faster.
In order to keep your body functioning properly and meet its daily needs, dietitians suggest about 60 milligrams of vitamin C per day.
Nevertheless, increasing that daily intake amount to 500 milligrams has the ability to increase your fat burning potential during exercise by 39%.
In fact, a study at the Scripps Clinic discovered that participants who ate half of a grapefruit with each meal during a 12-week time period lost an average of 3.9 pounds.

Coconut Oil
Since butter is a type of fat, many people have come to associate fats as being bad for your health.
While butter is indeed not a healthy fat, there are actually many fats called unsaturated that are necessary for the body, with one such unsaturated fat being oil.
In fact, an example like coconut oil is a fat that surprisingly helps increase your metabolism rather than slowing it down.
Coconut oil has a large amount of medium chain fatty acids which, compared to other fats, are more easily converted into energy.
That being said, coconut oil is less likely to be stored as fat in your body because of its unique composition and ease of conversion into energy.
As previously mentioned, the thyroid is the gland that controls the majority of a person’s metabolism.
Fortunately, coconut oil is extremely supportive of the thyroid, which additionally helps boost your calorie-burning mechanism.

Coffee
When feeling the need for a quick energy surge, lots of people turn to energy drinks and sugary foods.
Unfortunately, both of these choices will only increase your energy momentarily, only to come crashing down later because they are loaded with sugars.
Instead, a much healthier boost comes from coffee.
The caffeine in coffee (or even tea/espresso) gives your body a short-term increase in energy without the “crashing” side effect later on (as long as you don’t add spoonfuls of sugar to your drink).
Drinking one cup of coffee or just caffeine before a workout has been proven to result in better fat loss because it quick-starts your metabolism before you even begin to workout.
Your central nervous system becomes stimulated, which allows you to stay active and train harder for longer.
Additionally, coffee has shown associations for a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes due to the fact that it helps to break down the fat stored in your body.

Curry
For all spice lovers out there, the good news is here – the heat provided in a package of curry actually allows for an increase in your metabolism.
Eating something with as much spice as curry literally increases your body’s internal temperature, which allows you to speed up the fat-burning process, although only temporarily.
Furthermore, there have been recent studies which show that chemicals called isothiocyanates are present in particularly pungent types of foods like spicy mustard and horseradish.
These chemicals may actually assist in activating brown fat in your body and speeding up your metabolic rate.
With so many various spices included in curry such as ginger, hot peppers, cinnamon (which was previously mentioned), and turmeric, it is the “king” spice for boosting metabolism and killing calories.

Fish
Known for its abundance of omega-3 fatty acids and lean protein, fish is an obvious candidate for metabolism boosting.
Nutritionists recommend consuming more fatty fishes such as salmon because of their numerous fatty acids.
The omega-3 fats allow the body to decrease inflammation as well and lowering blood sugar, which in turn raises the metabolic rate.
Less well-known is the power of omega-3’s in fatty fish to decrease stress hormones.
When stress hormones are unusually high for elongated periods of time, the body begins to store fat and increase the blood sugar because it believes it is in “danger.”
By decreasing these hormones with ample servings of fish, the amount of stress hormones circulating through the body is dramatically lowered.

Grapefruit
For a long time, grapefruit has been associated with weight loss because it has the ability to lower insulin levels in the body.
When you consume too much sugar, your body recognizes this because sugar is simply accumulating in your blood and not being burned.
Therefore, the body releases insulin in order to take the sugar and store it, first as glycogen and then as saturated fat.
With its insulin levels being lowered by grapefruit, the body is less likely to become resistant to insulin, thereby becoming less prone to a disease like diabetes.
All in all, keeping your insulin at low levels will help your body store the fat when it needs in order not to become desensitized.

Green Tea
Scientists have identified a substance called Epigallocatechin gallate, a form of catechin, which is present in green tea.
Fortunately, this substance has been shown to increase the body’s fat burning process, thereby leading to a higher metabolism.
A study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition even discovered that “green tea extract boosted the metabolism by 4 percent over a 24-hour period.”
Although this may seem minuscule in the grand scope of things, one cup of green tea per day can actually help you lose an extra 70 calories.
If repeated over the course of a year, this practice can possibly lead to the loss of 5 pounds.
If such a regime is followed throughout several years, the results can be monumental.

Hot Peppers and Jalapeños
Chemicals in chili peppers called capsinoids have been proven to increase energy expenditures.
Capsinoids work by stimulating the body’s hormones and increasing heart rate, thereby making an individual breathe more rapidly.
Inn turn, this forces the body to burn more calories and fat.
As discussed previously, the heat from spicy foods like pepper and jalapeños increases your body’s internal temperature, which is helpful when trying to speed up the metabolizing process.
Furthermore, the peppers seem to assist in increasing satiety and decreasing your appetite, which is crucial for those looking to lose some weight.
Dietitians and nutritionists recommend one pepper a day, whether it is a jalapeño on a sandwich, red peppers in a salad, or hot ground pepper used to season leanmeat.

Lean Turkey
The idea of proteins being beneficial to an individual’s metabolism has already been emphasized.
However, both turkey and chicken are particularly special because they are extremely high in protein, but also extremely low in harmful fats – such a combo makes for a great source of metabolism-boosting.
According to sports dietitian Lindsay Langford, most normal proteins “will use 15-30% of the calories you consume in the process of breaking them.”
With chicken and turkey having amplified powers due to their lack of fats, this process of burning calories is magnified to an even further extent, displaying how these lean proteins are so helpful in improving a person’s calorie burning process.

Seaweed
Although it is not the most delicious-looking nor sweet-tasting food, seaweed contains an abundance of iodide which is extremely vital in maintaining your thyroid health.
The iodide in seaweed stimulates the thyroid to produce thyroid hormone throughout the body, which is a main component of regulating your metabolism.
If your iodide levels are too low, you run the risk of developing an underactive thyroid, leading to a sluggish metabolism and symptoms of fatigue.
Additionally, iodide serves not only as a hormone stimulant, but also acts as a bodyguard for the thyroid.
Each day we are bombarded by packaged foods, drinks, and environmental factors that expose us to free radicals.
These free radicals attack the entire body which includes the thyroid.
By regulating your iodide levels or at least maintaining them through supplements or foods, your thyroid is better protected from free radicals damage.

Spinach
Not only spinach, but most leafy greens, in general, can be assumed to be great metabolism boosters.
Because leafy greens do contain a high amount of fiber, they can actually increase your fat burning abilities by up to 30%.
Lori Kenyon Farley, a Certified Nutrition Consultant specializing in wellness, fitness, and anti-aging, suggests that individuals consume about 3 servings of leafy greens per day in order to see the most beneficial results.
In addition, spinach contains more than just fiber; it also contains a hearty load of iron.
The importance of iron in the body is crucial – it produces hemoglobin which is the protein in our blood that binds to oxygen.
Each hemoglobin can carry 4 oxygen molecules and it takes this oxygen to tissues throughout the body in order for our cells to carry out their specific metabolic functions.
In other words, less iron means a lower-functioning metabolism and vice versa.

Watermelon
Contrary to some beliefs that too much watermelon is detrimental due to its high sugar content, recent studies have shown that there are actually many health benefits that watermelon provides.
Increased fat burning is one such positive outlook because it contains a high concentration of an amino acid called arginine.
Interestingly, when a study published in the Journal of Medicine was conducted by supplementing arginine into the diets of animals, researchers found that over a 12-week time period, a sixty percent reduction in fat was observed.
This dramatic decrease was attributed to the fact that arginine has a special ability to increase the rate at which fat is metabolized while also increasing muscle mass simultaneously.
When both processes are paired together, it makes for a super-booster for metabolism.

Water
If there was one item in this list which was the easiest to come by and provided the most efficient way to increase your metabolism, water would probably be it.
It is the starting point for anyone trying to lose weight, boost metabolism, or even simply get healthy.
A study from the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism discovered that drinking water bolsters metabolic rate by 30 percent, which is a fantastic outcome considering all that is involved in the process is drinking a glass of liquid.
Water is such a prime metabolism booster because by consuming larger amounts of fluid, your body is better able to effectively break down fat and other stored nutrients.
When an individual is dehydrated, his or her metabolism slows down dramatically because it is not getting the proper amount of water.
Therefore, it assumes there is danger, leading to the storage of excess fats.
The only tricky thing with drinking water is knowing exactly how much you should be consuming.
Fitness expert Brad Davidson has found that drinking half your body weight in ounces is an ideal amount of water intake per day.
For example, a 140-pound individual should try to drink at least 70 ounces of water each day to start with.
Conclusion
Hopefully, it has become obvious that your metabolism has a lot more impact on your body, rather than just being “fast” or “slow.”
Clearly, the best possible ways to increase your metabolism are to eat healthy and exercise daily.
That means consuming leafy greens, vegetables, fruits, and the allotted daily servings of protein, fiber, carbohydrates, and other nutrients.
Notice, however, that following a diet or a strict-eating regimen is not included in this recommendation.
This is because, as previously discussed, your body needs a specific amount of energy to function correctly.
It retrieves that energy from the foods you eat and the environment that you expose yourself to specific to your individual lifestyle.
Nevertheless, exercising each day is likely the most effective way for an individual to boost his or her metabolism because not only does working out increase your calorie-burning, but it also relieves stress which is notorious for inhibiting metabolism.
Furthermore, your metabolism boosts both during and even after your workout; so you continue to expend energy even after you have finished exercising.
So, whether you have become chronically lethargic, are hoping to lose weight, or simply want to support your health, increasing your metabolism is most certainly the right place to start.
FDA Compliance
The information on this website has not been evaluated by the Food & Drug Administration or any other medical body. We do not aim to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any illness or disease. Information is shared for educational purposes only. You must consult your doctor before acting on any content on this website, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, taking medication, or have a medical condition.
HOW WOULD YOU RATE THIS ARTICLE?







Had no idea about so many factors affecting it. Great read
Hello Darnell! I’m glad you enjoyed the article:)
Sleeping is very important, totally agree with that 1
Which products could contain trans fats and how to idetify them on food labels?
Hello, Edward!
You should look for “partially hydrogenated oils” on the food label.