23 Evidence-Based Benefits of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)
You have likely heard of CoQ10.
However, you may not be aware of the vital role that this coenzyme plays in your health.
Taking CoQ10 is an effective way to boost your heart health, protect you from the side effects of certain drugs and help your body stay strong and healthy.
If you are not sure whether you need to take this coenzyme or what it can do for your health, we will explore the latest scientific research about how this compound affects your health.
We answer all your questions and provide you with the latest information about COQ10.
Understanding Coenzyme Q10
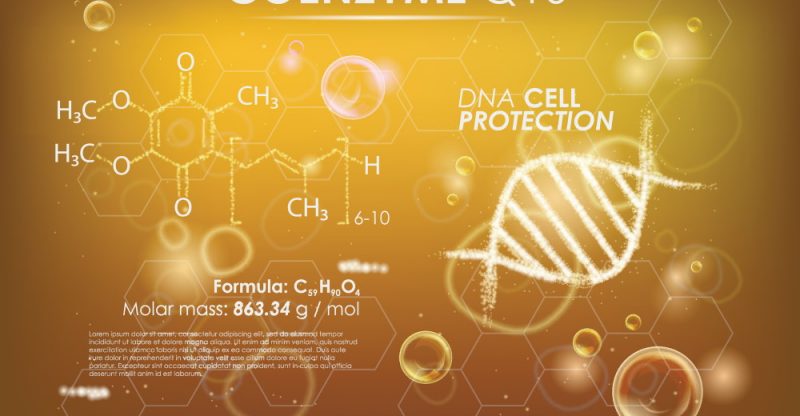
Coenzyme Q10, also known as CoQ10 or ubiquinone, is crucial to cellular health.
As a coenzyme, its primary function is to support other enzymes in carrying out their tasks.
You will find most of your body’s supply of CoQ10 in your mitochondrial membranes, where your cells make their energy (1).
By transporting electrons into your cell’s mitochondria, CoQ10 supports energy production.
This coenzyme is also a potent antioxidant found in lipoproteins, where it helps support cellular membranes and improve cell function (2).
The organs and tissues in your body that require the most energy have the most abundant supply of CoQ10.
These massive energy users include your liver, brain, heart, kidneys and skeletal muscles, so you will find more of this powerful coenzyme here.
Sources of Coenzyme Q10
Your body naturally produces about half of the CoQ10 you need to be healthy.
The remainder must come from dietary sources or supplementation.
Many of the foods with the highest concentrations of this compound are where it is stored in other animals, like the organs and muscle tissues of animals and fish (3).
You can also get smaller amounts of CoQ10 by eating dairy products, eggs, nuts, some vegetables, and legumes.
The Difference Between Ubiquinone and Ubiquinol
There are two forms of CoQ10 found within your body.
In its fully oxidized state, it is known as ubiquinone, and when fully reduced, it is ubiquinol (4).
The difference between these two is a gain or loss of electrons.
The ubiquinol form has the most antioxidant benefits for your health.
This form accounts for nearly all the CoQ10 in your blood.
CoQ10 is a fat-soluble compound, which means it is transported by lipids, like HDL and LDL.
As you age, you will have more ubiquinone and less ubiquinol, since your body converts these less efficiently over time (5).
Taking CoQ10 Supplements
Most CoQ10 supplements are ubiquinone unless they are labeled otherwise.
In most cases, doses of between 100 to 300 milligrams per days are useful for relieving the conditions described below.
However, in some cases, you may need a stronger dose to repair the damage or to treat specific diseases (6).
Talk with your doctor about what dose is right for you.
Because this coenzyme is fat-soluble, it is best absorbed by your body when it is taken with some amount of fat or when the supplement contains oil (7).
You can also increase absorption, by taking this supplement with either Vitamin E or C (8).
How your body processes this supplement, will depend greatly on your gut health and how well your system absorbs fat (9).
Low CoQ10
You may not be making or be consuming enough CoQ10 to support your body’s needs.
Several conditions and diseases can result in a deficiency of this vital compound, and your nutritional intake can also play a role.
Symptoms or Effects of Low CoQ10 Levels
If your levels of CoQ10 are just slightly lower than usual, you may experience symptoms such as muscle weakness or fatigue (10).
More severe deficiencies are usually caused by disease or specific medication conditions, which can appear at various points in your life.
The most common symptoms of a serious lack of CoQ10 include loss of balance or coordination, loss of hearing, damage to muscles or kidneys, a rash and even death if your deficiency is not appropriately addressed (11).
Reasons Your CoQ10 Levels May Be Low
What would cause a chronic deficiency in this crucial coenzyme?
If you have genetic mutations, mitochondrial malfunctions, or have increased oxidative stress from an autoimmune disease, then you may lack enough CoQ10.
If you have heart disease or heart failure, you could also benefit from supplementation.
The most common causes of low levels of CoQ10 in your system include:
- Cancer (12)
- HIV/AIDS (13)
- Sepsis (14)
- Diabetes (15)
- Hyperthyroidism (16)
- Low levels of testosterone (17)
- Obesity (18)
- Nutritional deficiencies (19)
- Asthma (20)
- Smoking (21)
- Taking statins (22)
- Chronic migraine headaches (23)
- Mental health disorders, like schizophrenia and depression (24, 25)
- Genetic mutations and disorders, including Phenylketonuria (PKU), Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS), and Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) (26, 27, 28)
- Acromegaly (29)
- Autoimmune disorders, like Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (30)
As you age, your levels of CoQ10 may also naturally decline.
Because this coenzyme is often stored in lean muscle, as you age and lose muscle mass, you may naturally also lost CoQ10.
Therefore, while aging does not directly cause the loss of this compound, it is more prevalent in older people and those with less muscle mass (31).
High CoQ10 Levels
Symptoms or Effects of High CoQ10 Levels
In some instances, your body may store too much CoQ10, putting you at risk for specific symptoms and disorders.
When you have too much of this antioxidant in your system, you may experience mitochondrial dysfunction.
You are also at an increased risk for developing breast cancer (32), having skin cancer spread (33), or dying from heart failure (34).
Reasons Your CoQ10 Levels May Be High
You are most likely to have high levels of COQ10 if you have fibromyalgia or hypothyroidism.
In the first situation, it is likely that the coenzyme is not able to enter cells (35) while in the second, the reduction in energy production in the mitochondria likely leads to the elevated levels of CoQ10 (36).
Coenzyme Q10’s Health Benefits
Researchers have been studying the effects and benefits of coenzyme Q10 for many years.
Among the varied ways that CoQ10 can improve your health is its ability to enhance your energy levels, protect your heart, reduce oxidative stress throughout your body and treat various diseases that are characterized by inflammation and oxidative stress.
The next section discusses what we can learn from medical research about this important compound, including why you may consider adding a supplement to your healthcare routine if you have certain conditions or risk factors.
Acts as a Powerful Antioxidant
In its reduced form, ubiquinol, Coenzyme Q10 acts as a powerful antioxidant to protect your cells from the forces of oxidative stress (37).
Even in its oxidized form, ubiquinone, however, this compound can still help protect your cells from free radicals (38).
CoQ10 works by bonding with the fats in cell membranes, where it prevents this porous outer layer from becoming damaged (39).
Because this coenzyme is fat-soluble, it binds to cholesterol molecules, which are prone to oxidation.
When these lipids become oxidized, they form dangerous plaques in your arterial walls, leaning to hardened arteries and heart damage.
Therefore, having higher levels of CoQ10 in your blood can help reduce this oxidation (40).
Lowers Risk of Heart Disease
By improving heart health and preventing harmful thickening of the heart’s walls, coenzyme Q10 can help reduce your risk of developing or dying from heart disease.
If you have heart disease or have had a heart attack, this compound can still improve your heart in many ways.
A type of heart disease, cardiomyopathy causes the heart’s walls to become abnormally thick.
Over time, this leads to arrhythmia and circulation problems.
Supplemental CoQ10 can improve heart function in those with this disorder (41), while also reducing the thickness of the heart (42).
For those with heart disease or heart failure, taking this coenzyme could help restore proper levels of CoQ10 in the heart, which are reduced when your heart is damaged or subject to high levels of oxidative stress (43).
Those with heart failure have a lower chance of dying when taking this supplement (44).
It also reduces the need to be hospitalized for your heart condition (45).
If you have ever had a heart attack, taking CoQ10 can also lower your risk of having another one (46).
When you start taking this supplement within three days of a heart attack, you can experience a more regular heartbeat, less pain and improved overall heart function (47).
Reduces Blood Pressure
Blood pressure plays a significant role in heart health.
When your pressure is chronically high, it puts a strain on your heart and causes the muscles to weaken over time.
Keeping your blood pressure under control is vital for protecting your cardiac health over time.
Several research studies have shown that supplements, with as much as 225 milligrams per day of coenzyme Q10, can help to reduce systolic (48) and diastolic (49) blood pressure as much as 12 percent for those with elevated blood pressure levels.
If your blood pressure is only slightly elevated, CoQ10 could still help you.
It has also been shown to lower pressure in those with mild hypertension (50).
The effects may be dose-dependent since one study did not show any effect when taking 200 milligrams per day for people with moderate to severe hypertension (51, 52).
Taking 600 milligrams per day also did not produce positive results (53).
Women who are pregnant are at risk for developing preeclampsia, or high blood pressure during pregnancy.
This condition causes swelling of the extremities and, if not treated properly, can also cause problems for the fetus.
Taking CoQ10 supplements could help women reduce their risk for developing this form of high blood pressure when taken during pregnancy (54).
Promotes Blood Vessel Health and Improved Circulation
When you have higher levels of nitric oxide in your blood, your blood vessels dilate more.
This results in improved circulation of oxygenated blood through your system.
When your blood vessels are healthy, they naturally produce nitric oxide, which prevents arterial narrowing and ensures proper blood flow from your heart.
Certain types of free radicals, known as superoxides, can inhibit the effectiveness of nitric oxide and reduce blood circulation (55, 56).
Coenzyme Q10 helps to neutralize the effects of superoxide and raise levels of nitric oxide, which boosts circulation.
In clinical trials, patients taking between 100 and 300 milligrams per day of CoQ10 saw improvement in the health of blood vessels, and better circulation (57).
This was accomplished by raising levels of enzymes which inhibit superoxide (58).
Reduces Lipid Levels
Another risk factor for heart disease and a contributor to heart problems is high cholesterol.
Your body naturally produces cholesterol, but you also consume it when you eat animal products.
There are two main types of cholesterol.
LDL is sometimes called “bad” cholesterol, which you want to be low.
HDL is called “good” cholesterol, which you want to be slightly higher.
Eating the right types of foods can help you balance the ratio between LDL and HDL cholesterol.
Those taking CoQ10 may see a reduction in total cholesterol and an increase in HDL levels if they have heart disease (59).
While this study showed no effects on LDL cholesterol, additional research indicated that this coenzyme might also reduce triglyceride levels (60).
Animal trials showed the CoQ10 helps to move cholesterol out of the blood by transporting it to the liver, where it is broken down and excreted from the body (61).
Reduces Inflammation
Coenzyme Q10 can help to lower inflammation levels by inhibiting inflammatory compounds.
This compound reduces the production of specific proteins (NF-κB) which control the DNA that directs the production of pro-inflammatory compounds, such as CRP, TNF-α, and IL-6.
Inflammatory compounds linked to diabetes and heart disease can be controlled by CoQ10, according to 2016 and 2017 research (62, 63).
These studies aimed to evaluate the effects of CoQ10 supplementation on inflammatory mediators and the inflammatory response.
The response was also noted in those with diabetes (64).
Inflammation is responsible for many chronic health conditions and diseases.
Lowering or eliminating the proteins that produce this immune system response, can alleviate symptoms and restore health for many people.
Provides Neuroprotective Benefits
Coenzyme Q10 plays a significant role in protecting the brain and reducing the impact of various diseases and neurotoxins.
This includes helping patients with Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s diseases, as well as other conditions.
Parkinson’s disease slowly destroys neurons that produce dopamine, which is a crucial neurotransmitter that helps to send messages throughout the nervous system.
Dopamine controls many key functions, including motivation, memory, attention and reward systems.
It also regulates body movement.
In those who are in the early stages of this disease, their mitochondria have lower levels of CoQ10 than those found in healthy people (65).
Taking this coenzyme could help protect these dopamine-producing neurons from degeneration (66).
In clinical trials, supplements were shown to slow both physical and cognitive decline (67).
However, these results may be dose-dependent, since similar results were not achieved with higher doses (68).
Another type of neurodegenerative disease, Alzheimer’s disease, could also benefit from higher levels of CoQ10 in the body.
Alzheimer’s is a form of dementia that is caused by a buildup of tau proteins and beta-amyloid plaques in the brain.
By reducing oxidative stress and controlling the build-up of these compounds, CoQ10 is vital for the prevention of this disease.
While early clinical trials did not show improvement in this disease while using this coenzyme, more data and research is needed in order to reach a thorough conclusion (69).
Unlike dementia and Parkinson’s, which tend to strike people later in life, Huntington’s disease generally starts early in life.
It is the result of a genetic disorder.
This disorder affects the mitochondria of the cells and results in both physical and mental symptoms.
By taking CoQ10 supplements, patients with this disease can improve the function of their mitochondria (70), improve mental capacity and increase their ability to perform daily tasks (71).
Animal trials have also yielded similar positive results (72).
Other diseases, including Friedreich’s ataxia and familial cerebellar ataxia, have also had some success in using CoQ10 to treat symptoms and lessen the effects of these diseases (73, 74).
CoQ10 can also help protect your neurons from damage from chemicals, such as insecticides (75) and neurotoxins (76).
Improves Blood Glucose Levels and Diabetes Outcomes
Diabetes is an autoimmune disease that results from elevated levels of sugar in the blood and can cause many chronic symptoms and, if left untreated, even death.
Doses of CoQ10 lower than 200 milligrams per day have been shown to reduce blood glucose levels in both patients with normal blood sugars, as well as those with high levels (77).
Similar doses were effective at reducing not only blood sugar but also insulin levels in obese patients (78).
In some studies, glucose levels did not change, but insulin levels were lowered (79) or insulin sensitivity was improved (80).
CoQ10 may help treat or even prevent diabetes by reducing oxidative stress within the cells that produce insulin, while also boosting antioxidant levels in other cells (81).
Those with diabetes can suffer from many negative symptoms, including nerve pain, numbness, muscle weakness, and tingling.
These various types of neuropathy improve with supplementation of CoQ10, in some cases (82).
Promotes Fertility
All cells rely on this vital coenzyme to produce energy in the mitochondria, including male reproductive cells.
Sperm count and motility are both important for conception.
Without sufficient levels of this compound, there will not be enough sperm or sperm will lack the energy needed to fertilize the egg properly (83).
By taking CoQ10 supplements, men in one study improved their fertilization rates (84), while others saw improvements in their sperm motility and count (85).
Similar results were noted in a 2004 study of 22 infertile men (86).
This coenzyme can also influence a woman’s fertility.
Women who are trying to conceive through in vitro fertilization need a healthy supply of eggs to increase their rate of success.
Poor ovarian reserve or POR is a condition where a woman’s supply of immature eggs is low or of inferior quality.
Women with POR who take CoQ10 have experienced an increase in the number of viable embryos, as well as the number of pregnancies and live births (87).
Animal trials also confirm these findings (88).
Reduces Depression
When you have depression, your mitochondria are not functioning correctly, perhaps due to low levels of CoQ10.
Those with depression can experience a reduction in depression symptoms as well as in stress hormone levels when taking this coenzyme (89).
Clinical trials have noted similar results, including a drop in fatigue, sadness, trouble focusing and in the overall severity of depressive symptoms (90).
Similar results have been seen in those with bipolar depression (91).
Could Help Treat Cancer
Some types of drugs used for chemotherapy can damage your mitochondria in the heart tissues, and taking CoQ10 can help protect these cells from damage or destruction (92).
Animal trials also show that this coenzyme can help to protect kidney cells from similar effects of chemotherapy (93).
Adding CoQ10 to your cancer treatment can improve your chances of achieving remission and of stopping the spread of the disease, while also experiencing fewer adverse effects to the treatment (94).
In addition to these benefits, the CoQ10 can also help to reduce the cancer growth rate and slow or even stop the growth of tumors.
This compound effectively increases oxidative stress in harmful cancer cells, while leaving normal cells unaffected (95).
It has even been shown to kill certain types of cancer cells in cell studies (96, 97).
More research is needed to understand how this coenzyme could help treat cancer in humans.
Protects from Aging and Sun Damage
Some evidence suggests that coenzyme Q10 could protect you from various effects of aging, including mental and physical decline due to its antioxidant capacity (98).
In clinical trials, those who took this supplement had improvements in their physical capacity, vitality and overall quality of life (99).
In addition, CoQ10 could help protect your skin from damage by free radicals and UV damage (100).
By lowering inflammation and boosting antioxidant levels, this compound can improve the look of skin and reduce the effects that UV damage can have on your appearance (101).
Treats Respiratory Diseases
COPD or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease causes breathing difficulties and lowers your levels of CoQ10.
When those with COPD take this coenzyme, they can improve their oxygen levels, lower their heart rate and exercise longer (102).
The same types of outcomes have been noted in those with asthma while reducing their need for corticosteroids to control their condition (103).
Lowers Gut Inflammation
Taking CoQ10 could help to alleviate inflammation and reduce damage to the intestinal lining from factors such as alcohol (104) and NSAIDs (105).
Coenzyme Q10 boosts gut antioxidant levels and protects your digestive system from these negative forces.
This could give hope to those with ulcerative colitis (106) and other inflammatory bowel diseases.
Promotes Healthy Liver Function
Chronic inflammation can cause many different diseases, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Reducing the inflammatory markers that lead to this condition is crucial, and CoQ10 can help to accomplish this goal (107).
In animal trials, CoQ10 reduced inflammation and liver enzymes, while minimizing damage from this disease (108).
Other Health Benefits
Among the many health benefits already discussed, having sufficient levels of CoQ10 can help your health in other ways.
- Migraines – Taking supplemental CoQ10 can reduce the severity, duration, and frequency of migraine headaches (109).
- Fibromyalgia – Taking this supplement can reduce the symptoms of fibromyalgia, including reducing pain, inflammation, fatigue, and depression (110, 111).
- Muscular dystrophies – Taking CoQ10 could help to delay muscle wasting and improve muscle strength and fatigue in those with certain muscular dystrophies (112).
- Mitochondrial function – in those with diseases that affect the mitochondria, taking this coenzyme can reduce some symptoms, including help to reduce muscle weakness, stiffness, and tremors (113, 114).
- Multiple sclerosis – Those with MS could experience less inflammation, fatigue, and depression. when they take CoQ10 supplements (115).
- Oral health – Those with gum inflammation (116) and dry mouth (117) have seen improvements in their symptoms and oral health when taking this supplement.
- Osteoporosis – By taking CoQ10, you could slow the loss of bone matter and improve new bone formation (118, 119), helping to prevent or treat osteoporosis.
- Peyronie’s Disease – Taking this supplement can reduce the scar tissue, pain, and curvature of the penis that is caused by Peyronie’s Disease (120).
Precautions
Most people who take CoQ10 supplements do not experience any adverse reactions.
When rare side effects occur, they are generally mild.
They include headache, rash, changes in appetite, upset stomach, nausea and diarrhea (121).
If you have reduced liver function, you risk accumulating too much of this coenzyme in your system over time.
This is because your liver processes this compound, and if this filtering organ cannot effectively remove it from your body, you can soon have too much.
This buildup can increase the risk and intensity of the side effects.
Interactions with Other Medications
If you take statins to control your cholesterol, you run the risk of becoming deficient in CoQ10.
A common side effect of these medications is muscle pain and weakness, which has been linked to low levels of CoQ10 in these tissues (122).
Taking supplemental coenzymes, while using statins can help reduce these side effects (123).
CoQ10 also helps reduce other side effects of statins, including the improvement of blood circulation and muscle strength (124).
Talk with your doctor about taking CoQ10, if you take statins.
If you take warfarin or any other blood-thinning medications, talk with your doctor before taking CoQ10.
Because this coenzyme is similar to Vitamin K, it can interfere with warfarin’s ability to prevent blood clots (125).
It also increases the rate at which these types of medications are flushed from your system, so it is essential that your doctor is aware of all the supplements you are taking (126).
If you take medicine for arrhythmia or heart failure, you could be at risk for elevated levels of CoQ10.
Medications that inhibit P-glycoprotein reduce your cells’ ability to pump CoQ10 from your cells, which can increase their concentration in your system (127).
Because CoQ10 can reduce blood pressure, it can increase the effects of medications designed for this purpose.
This can lower your blood pressure to dangerously low rates (128).
Since this coenzyme also reduces blood sugar naturally, taking it in combination with medications to lower glucose, can result in very low blood sugar levels (129).
Monitor your glucose carefully.
If you take medications for COPD or asthma, talk with your doctor about taking CoQ10, since this supplement can increase the time it takes for certain drugs to become effective in your system (130).
Conclusion
Coenzyme Q10 is a compound that is naturally made in the body.
It plays a crucial role in the mitochondrial function of your cells.
It helps to maintain cellular energy, reduce oxidative stress and lower inflammation in the body.
This can help prevent or protect you from several chronic illnesses.
Low levels of CoQ10 are associated with many different diseases and can be caused by nutritional deficiencies and medical conditions.
Even some medications can lower your levels of this important compound.
When your levels of CoQ10 are low, you are likely to have more inflammation, which can lead to heart disease, liver trouble, autoimmune diseases and much more.
CoQ10 keeps your blood pressure regulated, protects your brain cells from degeneration, reduces your risk of migraines and cancer and can lower your risk for heart disease, including cholesterol and blood sugar.
Most people have very few and only minor reactions to taking this supplement.
If you take certain drugs, like blood thinners, talk with your doctor before taking CoQ10.
FDA Compliance
The information on this website has not been evaluated by the Food & Drug Administration or any other medical body. We do not aim to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any illness or disease. Information is shared for educational purposes only. You must consult your doctor before acting on any content on this website, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, taking medication, or have a medical condition.
HOW WOULD YOU RATE THIS ARTICLE?