25 Evidence-Based Benefits of Beets
Beets are sweet, earthy, and versatile.
It’s no wonder people have been enjoying them for thousands of years.
Whether consuming the hearty root or delicious leafy greens, there is a lot to love about this popular root vegetable.
The beetroot comes in several different varieties and has even been made into specialty hybrids.
The most common beets are:
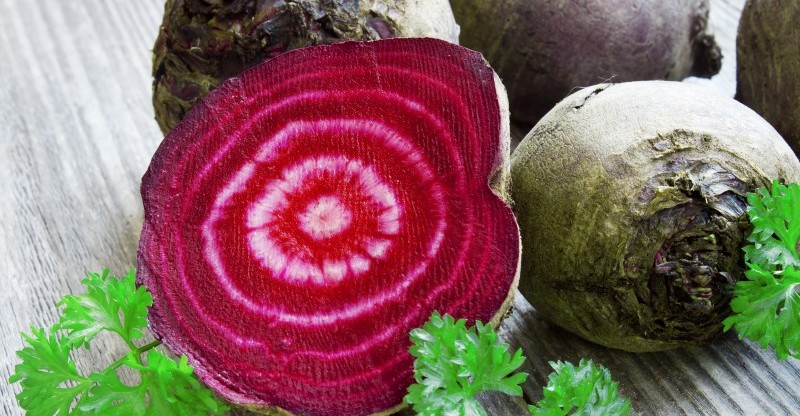
- Red beets. These are the most common beet. They appear dark purple in color and are commonly the ones found in cans or pickled at the grocery store.
- Chioggia beets. Named after an Italian fishing village, these beets don’t look special from the outside, but once you slice into the red and white swirled candy cane center you’ll be hooked. These beets have a charmingly unusual center that can be red or yellow in color.
- Golden beets. Golden beets are orange to yellow in color and have bright, flavorful flesh. These beets are not as sweet or earthy tasting as red beets. These are fantastic in salads or roasted in the oven.
- Sugar beets. These beets are purple or vibrant red in color and have a sweet root. In fact, table beets contain more naturally existing sugar than all other vegetables.
- Mangold beets. Sometimes referred to as “mangel-wurzel beets,” this variety is shaped differently from the rest. Taking on a parsnip or carrot appearance, this beet can reach upward of twenty pounds or more! They are yellow in color and sweet in flavor.
Beets are low in calories and fat-free.
In fact, a 2″ beet contains a mere 35 calories, 1.3 grams of protein, 6 grams of sugar, 2.3 grams of daily recommended dietary fiber, 8 grams of carbohydrates, 64 mg of sodium, 266 mg of potassium, 1% calcium, 5% vitamin B-6, 4% magnesium, and 6% vitamin C for the daily recommended value based on a diet of 2,000 calories.
No matter what type of beet you prefer, there are plenty of reasons to add them as a staple in your daily diet.
In this article, we will be considering all things beets, including how to store them, health benefits, precautions, and recipes.

History
Beets have been around for thousands of years, enticing people with their earthy, delicious flavor.
In the early years, humans would much rather eat beet greens than the root itself.
These greens were consumed in a similar way to Swiss chard or spinach.
Ancient Grecians and Romans were huge fans of beets, so much so that they tried to develop a growing method so that they could still eat beets out of season.
In ancient times, the beet was shaped more like a parsnip than the beet genus we know today.
The earliest record of the root consumption was in 1542 in Italy or Germany.
Despite new ways to prepare this delicious vegetable, it still took time for the beet phenomenon to kick in.
In time, Northeastern Europe began consuming beets as a dietary staple since it was one of the few vegetables that would grow during European winters.
Come 1747 there was a new way to use beets — sugar.
Berlin chemist Andreas Sigismund Marggraf began sugar extraction from beets (1).
These sugars were later used in tobacco, beet beer, and molasses.
Sometime later the first sugar beet plant was created, and the phenomenon grew.
Today, 20 percent of sugar comes from these sugar beets.
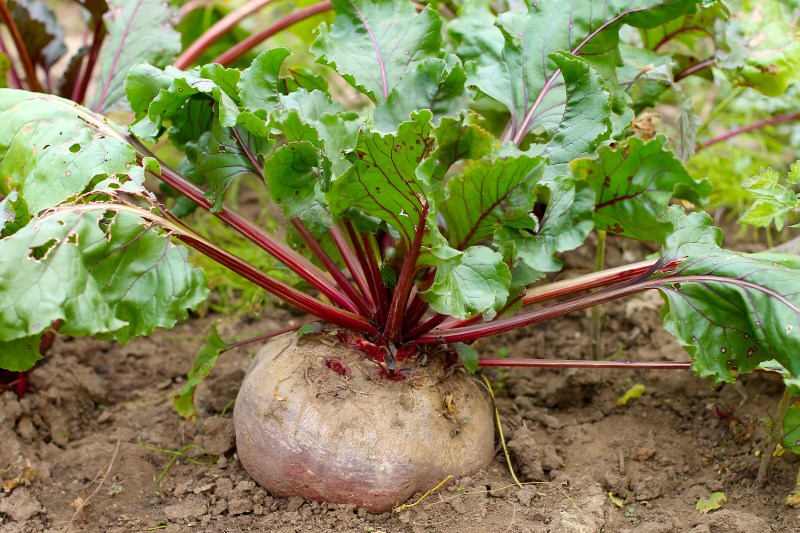

How Beets Grow
Known as the Beta vulgaris, beets are root vegetables, meaning they grow in the ground and are pulled from the soil when ripe.
Beet greens can actually be harvested before the bulb itself.
Beet greens are great in salads or fried in a pan.
If harvesting the greens before removing the bulb, be sure to leave some greens attached so that the beet can continue to grow.
Growing beets in your back garden is very easy, making them a perfect starter for new gardeners.
Beet seeds should be soaked before they are planted.
This will help them grow more efficiently.
Soak the seeds overnight before planting.
As a root vegetable, beets grow in the ground and are plucked from the dirt when ripe.
Beets do not take to cold soil, making spring or fall the perfect planting seasons.
Soil temperature should be at least 50° F to grow beets.
Plant your beets in a row, 1/2″ deep and three inches apart.
Unlike other vegetables, beets do not need a lot of space to take root.
They grow best when exposed to direct sunlight.
Soil should be kept free of rocks and properly enriched before planting.
You may want to plant several seeds in the same spot to ensure growth.
Beet seedlings need to be kept moist, so water them regularly.
When your beets grow to 3–7 cm in diameter, they are ready to be pulled.
Beets will actually fill your soil with nutrients as they grow, making them a fantastic garden partner for other seasonal vegetables.

Interesting Facts
Beets have a rich history. From Romans to brothels, here are seventeen fun facts about beets.
- Beets can be consumed raw or cooked.
- Beets were considered a strong aphrodisiac by the Ancient Romans. Since beets improve circulation, they were thought to aid with sexual dysfunction in males. Beets also increase hormone production in both sexes.
- Due to poor salt supplies, some cities actually use beet juice as an alternative for melting ice in the winter. Not only is this an eco-friendly option for keeping the roads safe, but it’s also better on tires than damaging salts (2).
- Dwight, from the television show The Office, was a beet farmer.
- The official Pompeii brothel, the Lupanare, was decorated with pictures of beets.
- The sugar beet is Utah’s historic state vegetable (3).
- According to Greek mythology, Aphrodite, the Goddess of Love, ate beets to appear more desirable.
- Beets were eaten during the Middle Ages as a cure for digestion issues and other illnesses as well as garlic breath!
- Beets are known as nature’s candy.
- The world’s largest beet on record weighed more than 156 pounds.
- Beets are said to be an eco-friendly solution for curing dandruff. Boil beets and let the water cool. Once cooled, massage the pink water into your scalp daily for a “greener” solution to dandruff.
- Forget spoons! In 1975 Apollo 18 astronauts were welcomed by the USSR cosmonauts by serving them beet soup while they were in zero gravity.
- In Australia, pickled beets are used as a hamburger topping.
- Assyrian texts dating back to 800 BC report beets growing in Babylon at the hanging gardens (4).
- Blondes, rejoice! You can actually use beet juice to dye your hair red/purple/pink. This will wash out.
- In 1801 the first sugar beet factory was opened by Frederick William III of Prussia (5).
- There is such a thing as beet wine.
Health Benefits of Beets
Fun facts aside, beets are packed with nutrition and health benefits both physical and mental.
Beets are good for just about everything you can find in your body.
Liver, kidneys, bones, brain, and eyes are all affected by the amazing health benefits found in this terrific root vegetable.

Low in Fat and Calories
Beets are low in fat and calories, having a mere 0.2 grams of fat and forty-three calories per one hundred grams.
Beets also contain healthy carbs and dietary fiber that will help you maintain energy throughout the day.
Beets and Copper
Copper helps human growth, production of eye and hair pigments, builds connective tissues, absorbs iron, and helps keep skin looking young and healthy (6).
Copper contains anti-inflammatory properties that can help ease symptoms of arthritis.
This mineral is also widely considered a brain food since it stimulates brain function.

Beets and Manganese
Manganese contributes to healthy bones, bone growth, creates enzymes and connective tissue, calcium absorption, and helps proper thyroid and hormone function.
Manganese is also responsible for regulating blood sugar and metabolism (7).
Beets and Vitamin C
Beets contain vitamin C, one of the best-known vitamins.
This healthy vitamin protects against prenatal health issues, diseases of the eyes, wrinkles, and immune system deficiencies (8, 9).
Common uses of vitamin C include stress relief, protecting against the common cold, and fighting the signs of aging.

Beets and Iron
There is 0.8 mg of iron per hundred grams of beetroot.
Iron is essential for muscle health and carrying oxygen throughout the body.
Oxygen is essential for brain and muscle function and is carried along by the formation of hemoglobin.
Iron also transports electrons (10).
Beets and Vitamin B6
Beets contain vitamin B6, which may help with premenstrual syndrome, arthritis, and nerve injuries, such as a carpal tunnel.
Vitamin B6 also contributes to healthy metabolism and an immune system and controls hormone levels (11, 12, 13).

Beets and Folate
Beets contain folate, which helps in repairing and synthesizing your DNA (14).
Folate also promotes tissue and cell growth.
Folate is great for sperm health, heart health, and your colon.
Beets and Dietary Fiber
Dietary fiber is important to your health.
This roughage is not digested like the rest of your food.
Instead, fiber passes through the body while passing on nutrients.
Fiber is the main source of maintaining healthy bowel movements and avoiding or curing constipation.
Fiber also lowers your cholesterol, controls blood sugar, and helps you maintain a healthy weight (15).

Beets and Potassium
Bananas are often thought to be the leader in healthy potassium.
Did you know that beets come in a close and healthy second?
There is 358 mg of potassium in bananas and 325 mg in one hundred grams of beets.
That’s only a 33 mg difference!
Potassium is great for your body and may help prevent kidney and heart disorders, stress, high blood pressure, stroke, and issues with the nervous system (16).
Beets and Sex life
Beets have a positive impact on your sex life.
Not only do beets improve erections, but they also act as a natural aphrodisiac. An aphrodisiac refers to any food or drink that causes sexual excitement or stimulates desire.
Oysters, figs, chili peppers, honey, chocolate, and beets are all well-known aphrodisiacs.
Because beet nitrates naturally encourage blood flow, beets have become an all-natural alternative to viagra.
Beets also contain boron, which is a metalloid chemical element that is directly responsible for the production of sex hormones.
Regular consumption of beets will help genitals retain increased circulation (17).

Beets and Blood Pressure
Life can be stressful, which affects blood pressure.
High blood pressure may lead to other serious health issues, such as stroke, memory loss, angina, artery disease, kidney damage, loss of vision, heart attack, and heart disease.
High blood pressure often has no symptoms, making it important to keep an eye on your blood pressure levels.
Beets are high in nitrate, which turns into nitric oxide once inside the body.
This gas contains anti-platelet properties that prevent blood clotting and thickening.
Adding beets to your daily diet may have a positive impact on your blood pressure.
In fact, a 2012 study suggests that drinking beet juice can lower your blood pressure within a mere 6 hours of ingestion (18).

Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Ever wonder how beets get that intense red color that can seemingly stain everything in your kitchen?
Beets get their color from a natural pigment called betalain.
This pigment acts as an all-natural anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, fungicidal, and detoxification substance.
Natural inflammation in the body can be a good thing.
For example, natural inflammation alerts the body to illness or injuries and kills bacteria and viruses, but chronic inflammation can negatively affect your health.
It can lead to allergies, autoimmune diseases, and perhaps cancer.
Inflammation that leads to swelling in the brain may even cause death.
Inflammation can also break down important tissues in the body.
Beets will act as a natural anti-inflammatory (19).
Prenatal Goodness
Pregnant women can get a boost of prenatal vitamins from beets, which are high in vitamin B folate.
Vitamin B is integral to the development of infant bones and spine.
Getting proper folic acids, such as those found in beets, can help prevent birth defects, including spina bifida.
Eating just three raw beets gives a woman more than 70% of her recommended folic acid a day.
Cooked beets have a lower level of vitamins and minerals but are still a great addition to your diet, especially while pregnant (20).
Healthy bone development aside, beetroot is also great for boosting immunity while pregnant.
These natural antioxidants will help a pregnant woman fight against potential infections.
Regulating metabolism is another benefit of eating beets while pregnant.

Beets as Hangover Cure
Symptoms of a hangover include nausea, light sensitivity, headache, dizziness, irritation, fatigue, and vomiting.
Beetroot juice is great as a natural anti-inflammatory for the body (21).
Beets also help clean the liver and banish any toxicity from the alcohol.
Consume by juicing, or use raw in a smoothie for an instant pick-me-up.
Beets and Liver Health
The liver is responsible for many important jobs inside the body, which is why it is so important that you take care of it.
As the largest solid organ in your body, your liver is responsible for producing bile, storing energy, and cleaning your blood.
The liver removes harmful toxins from the blood.
Processing vitamins and minerals from the bloodstream is another job done by the trusty liver.
Regularly eating beetroot promotes a healthy liver.
In fact, eating beets helps remove hardened bile, gallstones, cholesterol buildup, and other waste that forms inside the liver.
Beets are an excellent way to detoxify this bodily organ (22).

Beets and Anti-Aging
Beets may be your all-natural alternative to Botox!
Beets have lots of fiber, iron, carotenoids, antioxidants, vitamin C, and potassium.
These ingredients are key for looking and feeling younger.
High levels of folates and anti-inflammatory properties found in beets may actually reduce the visibility of wrinkles (23).
Anti-Inflammatory properties and vitamin C make skin appear younger and fuller.
Beets can be applied topically or ingested through juice for these fantastic results.

Beets and Bad Cholesterol
Beets are high in soluble fiber and contain no cholesterol.
In fact, beets may help lower bad cholesterol, or “LDL.”
Beet fiber not only reduces bad cholesterol, but also the triglycerides found in beets will increase good cholesterol (24).
Antioxidants in beets can help lower the harmful effects of bad cholesterol in the blood.
Beets will also prevent bad cholesterol from oxidization.
Aside from lowering harmful LDL, these antioxidants will also clear buildup from the arteries and eliminate LDL cholesterol from other areas of the body.

Beets and Cancer
Raw foods have been used for years to treat cancer, and beets are no exception.
Starting back in the 1920s, beetroot was used by German doctors Schoenenberger and Farberse as a treatment for cancer.
Ten years later a Hungarian professor would begin experiments connecting improvement of cancer patients with beetroot treatments.
Beetroot strengthens cells with increased oxygen and nutrients (25).
Beetroot’s high iron content is also responsible for its cancer-fighting properties.
Other studies have revealed that the betanin found in beetroot significantly decreased cancer cell growth and visibility.
These studies include prostate, pancreatic, and breast cancer.
Beetroot juice is said to have an anti-tumor effect and will detoxify the body while promoting healthy cell regeneration (26).
Stamina and Exercise
Beetroot will give your body power and energy throughout the day, which is great for those hitting the gym before heading to work.
Beetroot widens your blood vessels and increases blood flow.
This means that your muscles don’t have to work as hard since they’re not straining to get oxygen.
Beetroot will help your muscles work more efficiently and improve your overall performance (27).
This is especially useful for runners who are looking to run faster without burning out.
Beet juice will also aide in quick muscle recovery.
Try adding raw beets or beet juice to your power smoothie two hours before working out and see the effects this purple power food will have on your performance.

Beets and Heart Health
The fiber found in beets actually reduces the triglycerides in your body by pumping up HDL, or “good” cholesterol.
Triglycerides increase the risk of heart problems, such as heart disease.
Beets are also full of potassium, which aids in muscle contraction, including essential contractions of the heart.
You can reduce your risk of developing cardiovascular disease or a future stroke by including beets as a regular part of your diet.
One study of nine patients suffering from heart failure were given concentrated beet juice.
Within two hours, patients showed an increase in muscle strength by 12 percent.
The study showed that beet juice worked quickly and efficiently (28, 29).
Beets and Fatigue
Iron deficiency is one of the most common deficiencies in the world.
Luckily for beets lovers, beetroot is rich in iron.
Iron deficiency is the main source of anemia, which has such symptoms as fatigue, headaches, temperature sensitivity, and weakness.
Iron is like a one-man mineral army in your body.
Aside from staving off anemia, iron is responsible for muscle and hemoglobin formation and distributing oxygen throughout the body.
Oxygen is important for brain health and helps fight fatigue (30).

Dementia and Alzheimer’s
Beets are brain food, and eating them may slow the effects of dementia, which is caused by nerve damage and loss of nerve cells in the brain.
Dementia and Alzheimer’s can also be caused by stroke, a brain tumor, or other head injuries.
Beetroot contains a high amount of nitrates.
These then open the way for oxygen and blood flow to reach areas of the body that don’t get enough.
This blood flow includes the brain and the frontal lobes, a prominent area that degenerates as dementia sets in.
The folic acid in beetroot may also help protect against Alzheimer’s by preventing damage to the hippocampus (the area of the brain devoted to memory and learning) (31, 32, 33).

Beets and Bones Health
Want stronger, healthier bones?
Beets contain vitamin C, manganese, copper, folate, and magnesium, which are all vitamins and minerals that contribute to healthy bones and cartilage.
Beets also contain silica, a mineral that allows the body to absorb and use calcium.
Together, these health benefits of regularly eating beets can help improve the strength of your muscular-skeletal system.
Beets can also reduce your risk of osteoporosis.
Avoid eating beet greens for bone health, as they are high in oxalate and may reduce calcium absorption (34, 35).

Beets and Depression
Beets contain tryptophan, which is a mood-altering chemical.
In the body, the brain will transform tryptophan into serotonin, which can have a direct impact on your mood, memory, social behavior, sexual desire, appetite, sleep, and more.
Beets can impact your mood the same way as chocolate.
Raw beets also contain more than 30 percent of your daily recommended folate needs.
People suffering from depression or insomnia often have a folate deficiency.
If using beets for depression, be sure to use them raw.
Using beets in their freshest form will ensure you are getting the most folate from them (36).
Beets and Eyes
Beets contain a form of vitamin A called beta-carotene.
This vitamin can help prevent cataracts and blindness associated with age.
Beets also contain lutein and zeaxanthin, which are extremely good for the retina.
As well as being a powerful antioxidant, healthy beets may also aid in the reduction of macular degeneration (37).

How to Buy and Store
Because beets are so good for you and so easy to use in recipes, it makes them a great vegetable to have fresh in the fridge or waiting for you in the freezer.
So, how do you know if beet is fresh and ready for purchase?
Choose beets with rich red color and feel heavy for their size.
Avoid beets that show signs of wear, such as nicks or bruises.
Beets should feel firm to the touch and have a bright green top that is still attached.
Selecting a uniform size for your beets contributes to even cooking.
Beets can grow very large, however, so stay close to baseball size and under to ensure the freshest flavor and the most nutrients.
Because beets are root vegetables, they will need to be gently scrubbed under running water to remove any grit or dirt.
Note that this should only be done before consumption.
If you are simply storing your beets for future use, do not scrub them, as this may promote quicker deterioration.
When it comes to standing the test of time, root vegetables seem somewhat invincible.
How can you tell if beet has gone bad?
Beets that have spoiled may be soft, slimy, and easy to puncture with your finger.
Avoid early spoiling with proper storage.
Once you have your beets home, you’ll want to store the ones that you aren’t using.
Beet stems, while bright and crisp, will suck moisture and nutrients from the beet and should be cut off before storing.
Leave only two inches or so of taproot on top of the beet so that your beets won’t “bleed” while being cooked.
Beets and separate beet greens should be placed in a plastic bag and refrigerated in the crisper.
If kept in a cool compartment, beets will keep for one to two weeks.
Beets stored in the freezer will last up to one year.
Simply wrap them in a food bag meant for freezer storage and place them in your icy freezer.
For extra insurance, seal your beets in a freezer bag and then store inside of an airtight container.
Don’t forget to label your plastic bag with a date and item description so that you can easily find them.

How to Add Beets into Your Diet
As beets are an acquired taste, you may have to be creative to start enjoying them.
Always have them readily available in the house.
Roast your beets, peel the skin and store in your fridge.
You may also want to cut them into cubes to be stored in the fridge or freezer for easier meals.
Having them prepped and ready allows you to throw them into a salad or your juicer at a moment’s notice.
Frozen beet cubes are also fantastic for adding to a smoothie in the morning.
Here are eight more ways to enjoy beets.
- It may sound odd at first, but beets actually taste delicious in desserts. Add these healthy vegetables to your brownies or chocolate cakes by substituting the same amount of butter for pureed beets. Healthy and delicious!
- Beet supplements. Beet capsules can be purchased at natural health food stores and pharmacies. Talk to your doctor before choosing a beetroot supplement.
- Pureed beets also make great sauces. Fill your food processor with pine nuts, basil, olive oil, and cooked beets for an unforgettable pink pesto that’s packed with vitamins.
- Shredding your beets raw or cooked makes it easy to include healthy beets in your meals. Shredded beets can easily top a pasta salad, green salad, quinoa bowl, pizza, or bruschetta.
- Beet wraps are easy to make and taste great with any sweet or savory filling. Mix a finely grated beet into your usual wrap or pita recipe for a fun and pink flatbread.
- Mix beets with your usual deviled egg recipe to wow your guests with fantastic color and flavor.
- Frozen beet yogurt is a great take on sweet and savory desserts. Stir Greek yogurt, mashed beets, honey, olive oil, and a hint of salt to combine and pop into your ice cream maker. This is a great spin on a summertime treat with a flair for color.
- Mix chopped beets in with your usual morning smoothie or protein shake to reap their health benefits.
- Use beets in your sandwiches. Turkey, beets, and Swiss cheese is a real crowd pleaser.
Precautions
Have you ever heard the saying “too much of a good thing”?
This may be the case for beets.
While beets are an excellent source of nutrition, there are a few things to keep in mind if you’re going to be eating this fantastic root vegetable.
Beeturia
Beets discolor your urine and your stool.
If you’ve been eating a lot of beets recently and happen to notice that your urine is pink, don’t worry!
Why do beets turn your pee red?
Beets are full of compounds called betacyanins, which gives the beet its color.
Science suggests that when the compound betanin reacts with your stomach acid, it can actually affect the color of your waste!
This is referred to as “beeturia” and is completely harmless (38).
Can Beets Give You Gout?
Beets have a considerable amount of oxalate, which increases uric acid and may contribute to a very unpleasant condition called gout, which is caused by a buildup of uric acid.
This acid then forms small “crystals” in your tissues, resulting in intense pain.
Famous gout sufferers include Henry VIII and Alexander the Great.
Gout is a metabolic disease that results in severe arthritis, especially in smaller joints and the feet, ankles, and knees.
Symptoms of gout include pain, swelling, fever, chills, and tophi lump around the hands, knees, feet, elbows, or ears (39, 40).
Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are caused by a buildup of insoluble calcium and create a painful mass in the kidneys.
Beetroot is rich in oxalate, which can create calcium oxalate stones.
People who are predisposed to forming stones should stay away from beet consumption as much as possible (41, 42).
Unhealthy Iron Buildup
Beets are full of iron and copper minerals.
While otherwise healthy for you, those suffering from certain diseases, such as Wilson’s disease or hemochromatosis, will want to avoid any foods that contain an excess of iron.
Regular consumption of beetroot for those suffering from iron overload may worsen your existing condition (43).
Avoid Beets during Pregnancy
While beets are full of healthy properties and vitamins, they may not be the best thing for a growing mother-to-be.
Beetroot contains betaine, which may have a negative impact on a growing fetus (44).
Other Side Effects of Beet Consumption
Although natural and healthy for you, some people may experience a negative reaction to consuming beets.
Negative side effects include headaches, chills, nausea, weakness, vomiting, and pain in the abdomen (45).
If you experience one or more of these side effects while eating beets, stop eating them.
Just remember to find another way to get a high dose of vitamins and minerals.
You may also consider taking beetroot supplements after consulting your family doctor.

Conclusion
Beets are great for your health, and they’re delicious.
What better combination could there be?
FDA Compliance
The information on this website has not been evaluated by the Food & Drug Administration or any other medical body. We do not aim to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any illness or disease. Information is shared for educational purposes only. You must consult your doctor before acting on any content on this website, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, taking medication, or have a medical condition.
HOW WOULD YOU RATE THIS ARTICLE?







I know that beets are used for sugar production. Considering this fact, I wonder if people with diabetes can enjoy the benefits of beets?
Is it true that beets juice can be harmful?
Do beets lose their qualities after boiling?
Are there any beneficial elements in beets peels?
A very interesting article, full of information and well worth the read. Thank you.
excellent about the beet